The PDCA cycle have been widely applied to a variety of processes and industries: running manufacturing plants, restaurants, projects, services, and so on. PDCA is a popular problem-solving technique in total quality management which had also been successfully used in Toyota's production system in 1960s.
The Use Cases of PDCA cycle
Explore and understand the effects of different solutions in a controlled environment
Minimize waste through small-scale testing prior to full implementation
Test different approaches to the improvement process to find out what works for the organization
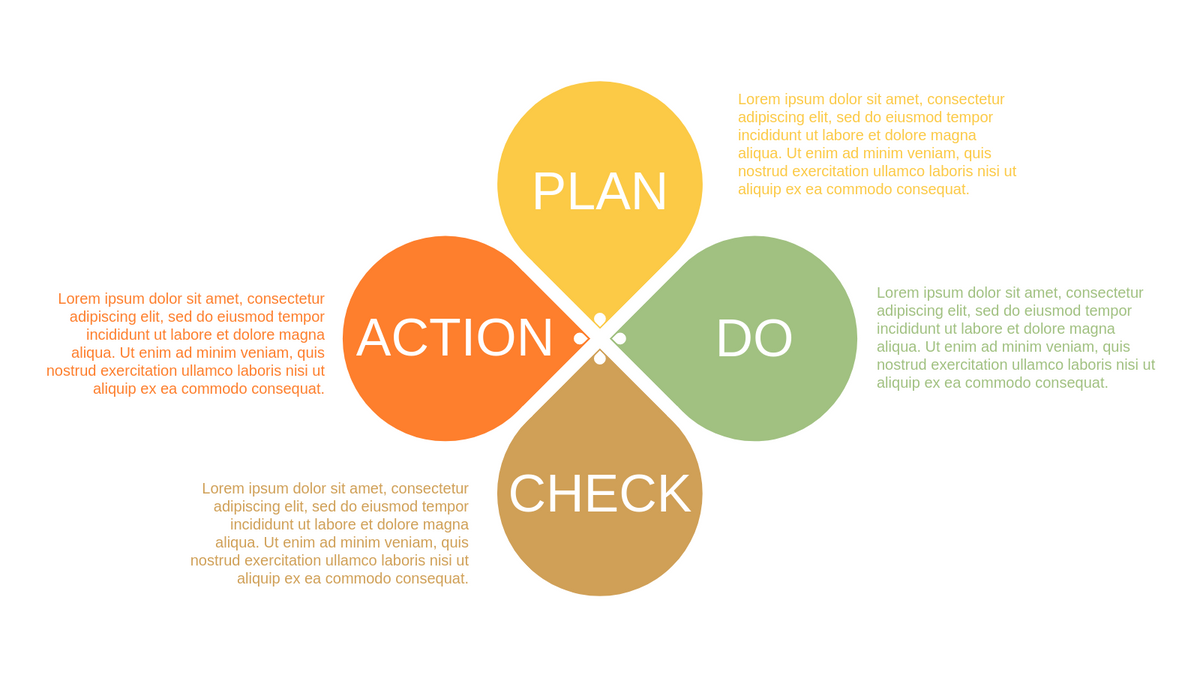
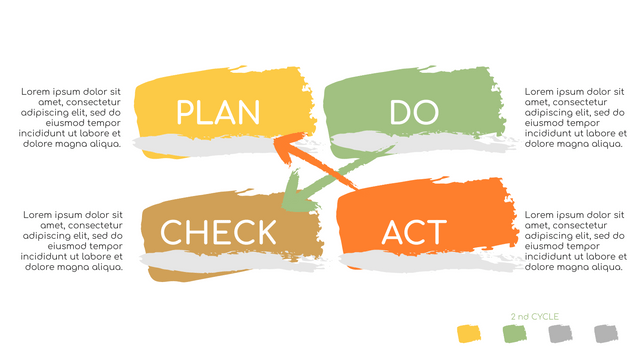
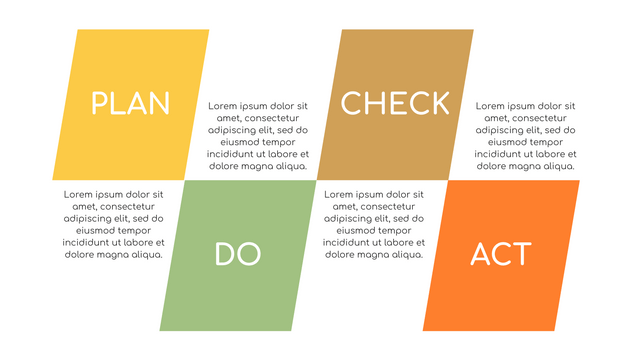
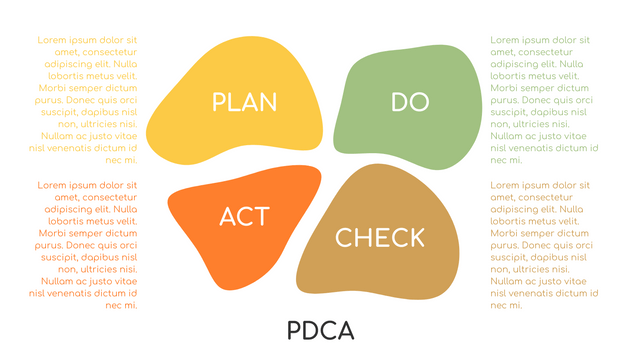
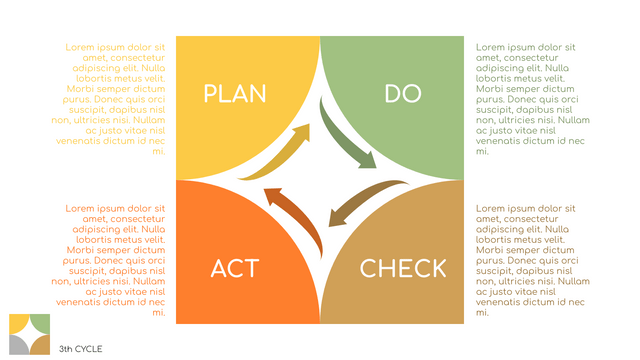
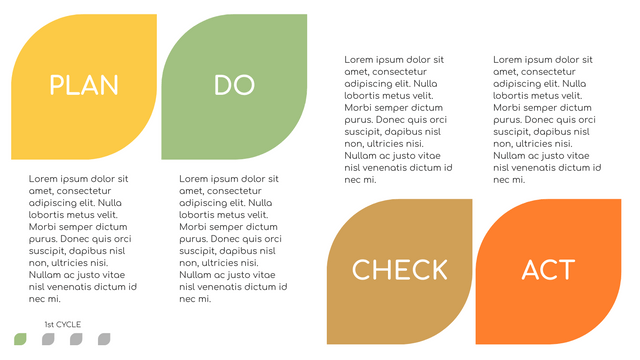
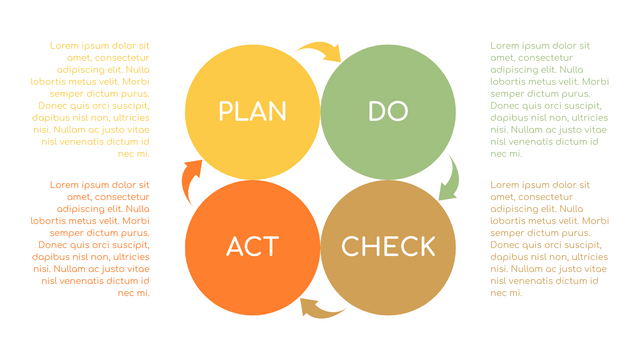
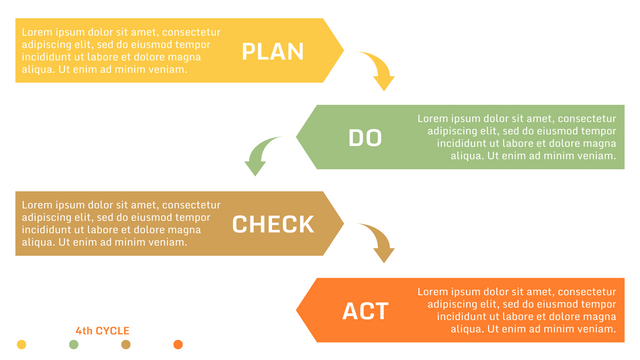
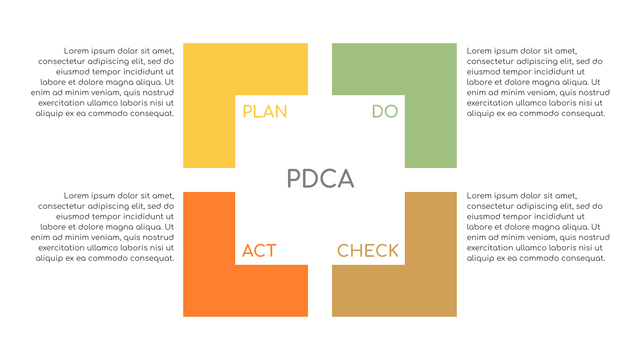
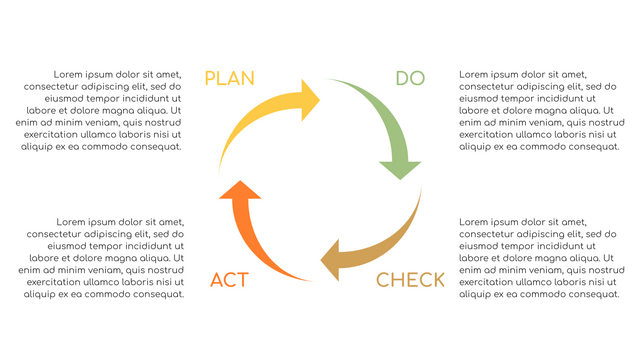
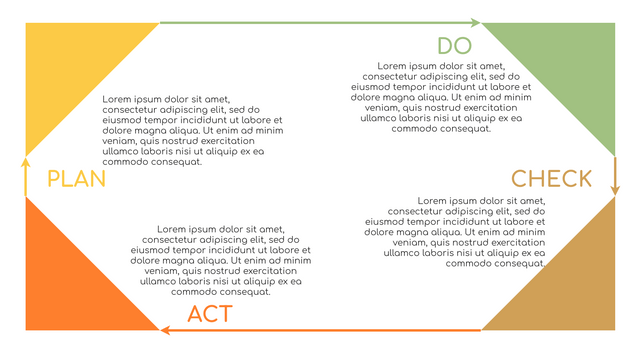
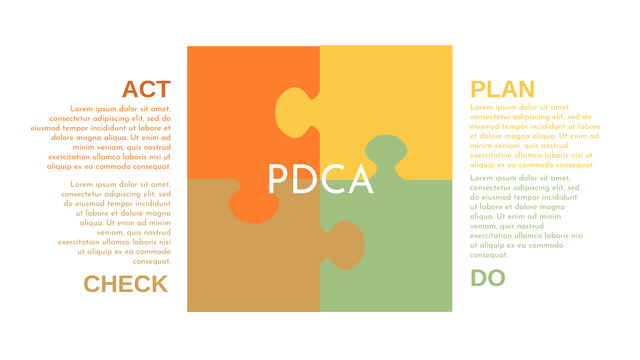
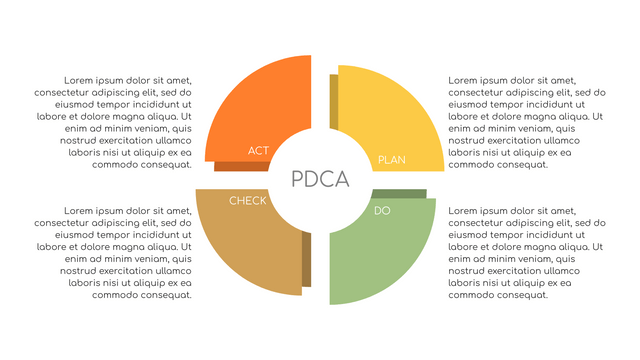
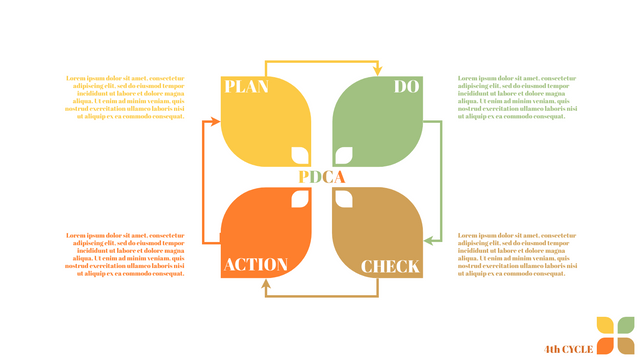
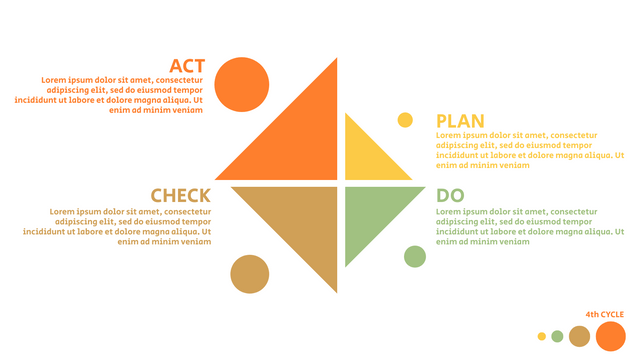
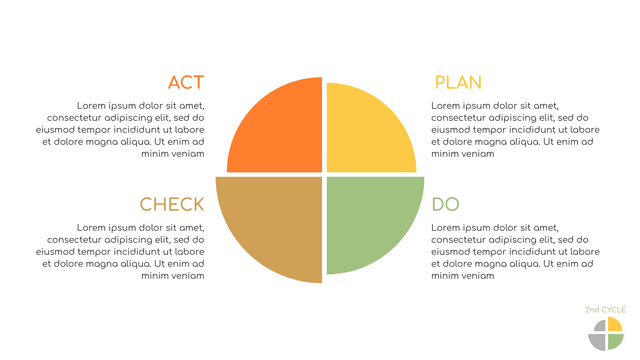
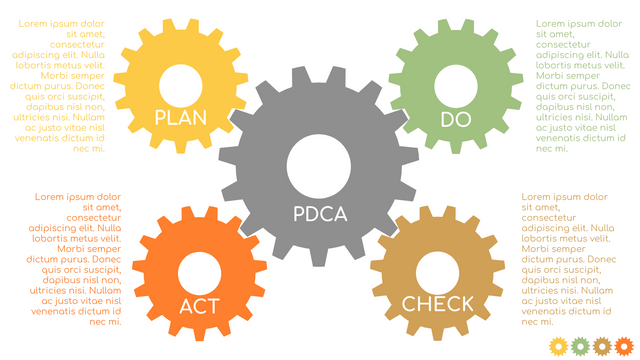
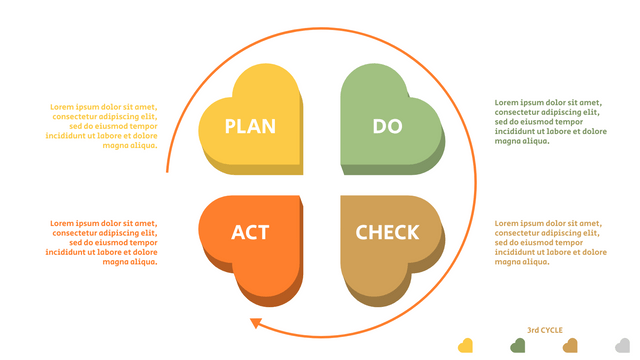
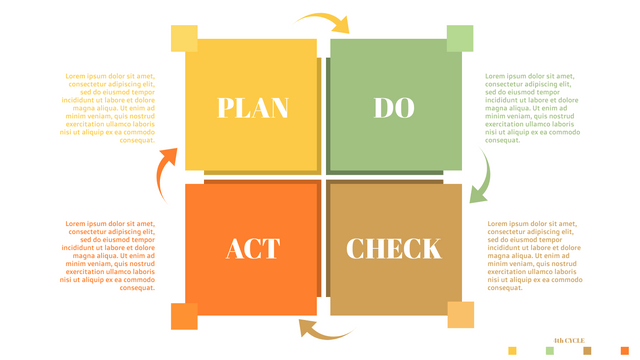
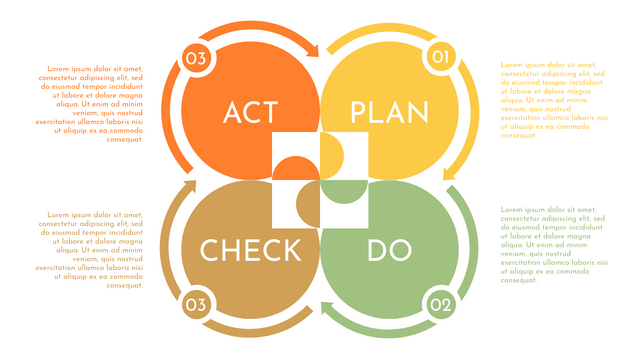
What is PDCA Cycle?
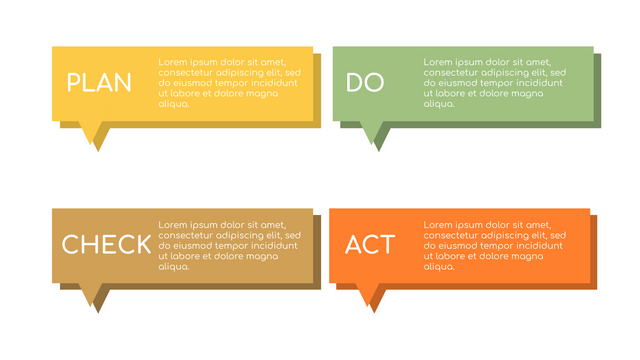
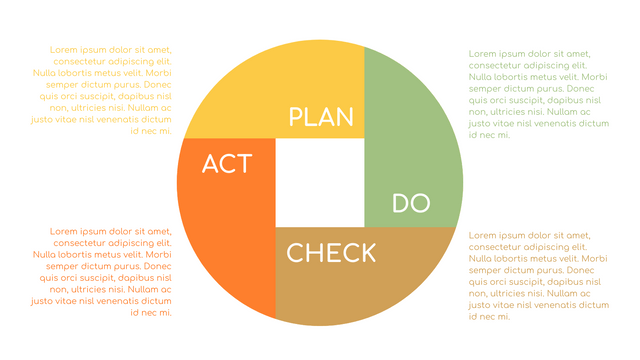
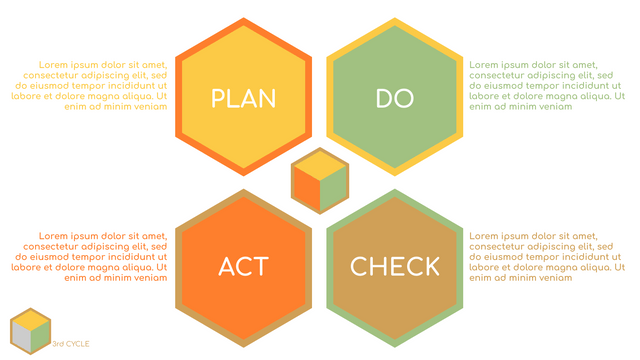
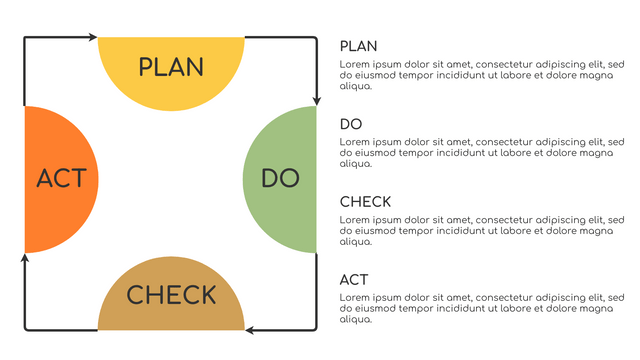
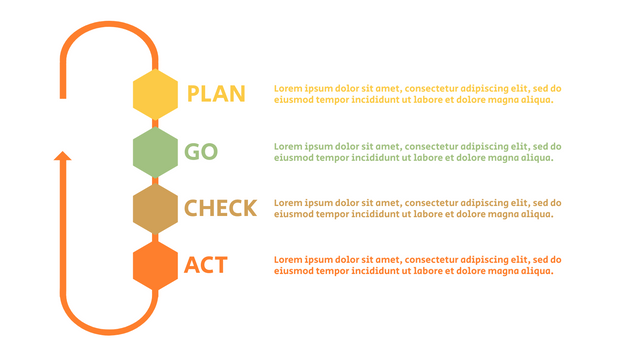
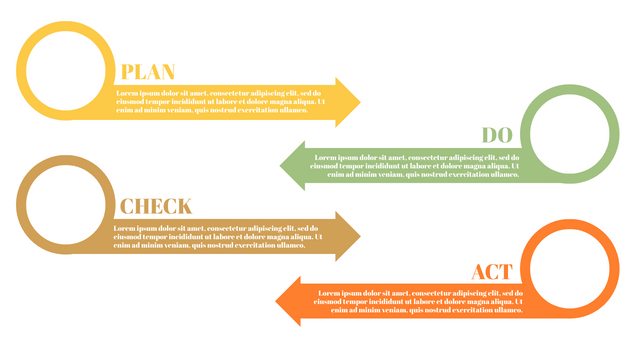
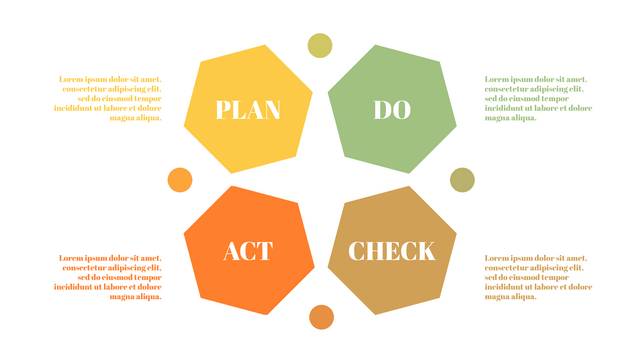
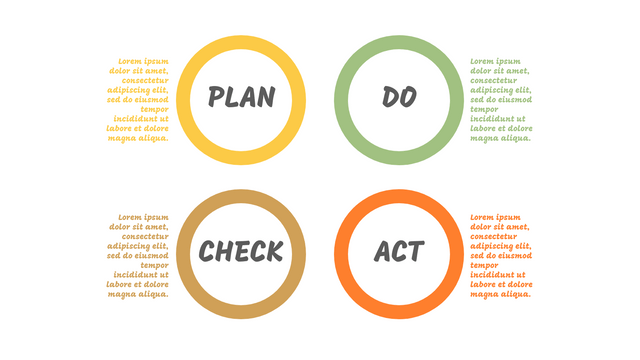
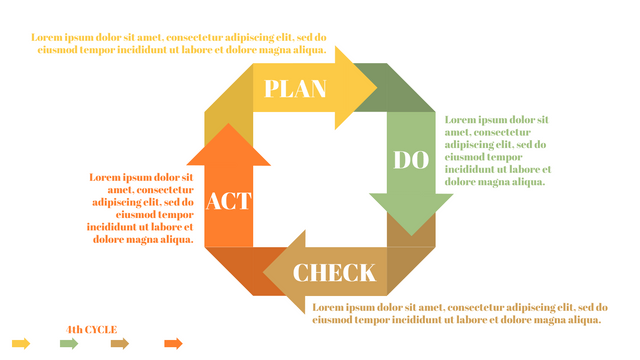
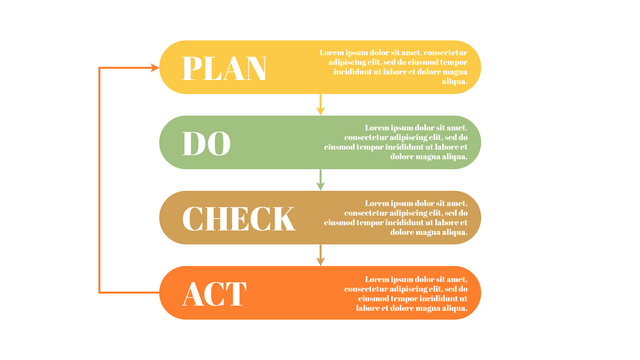
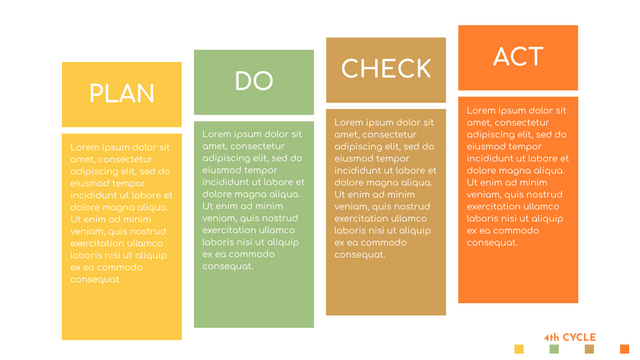
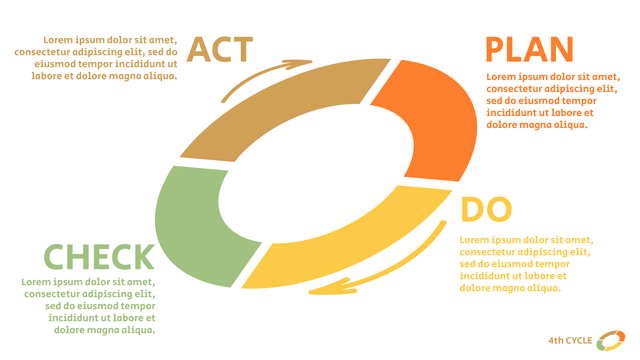
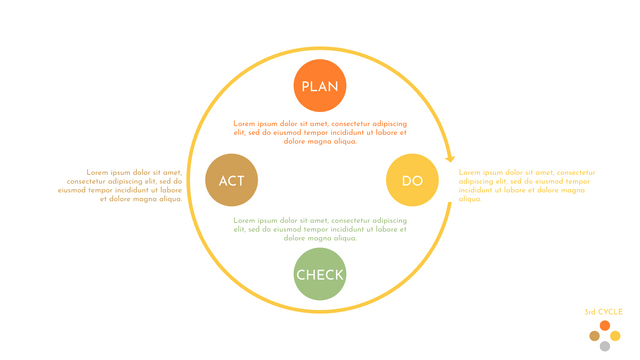
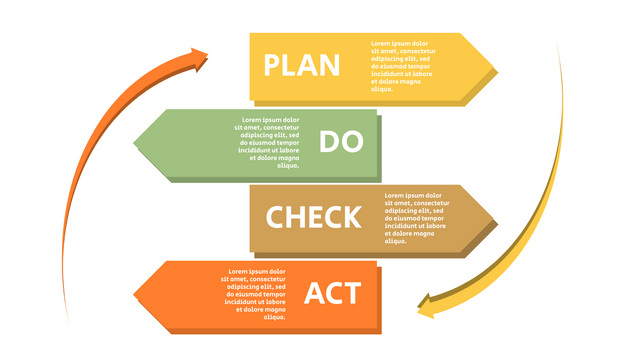
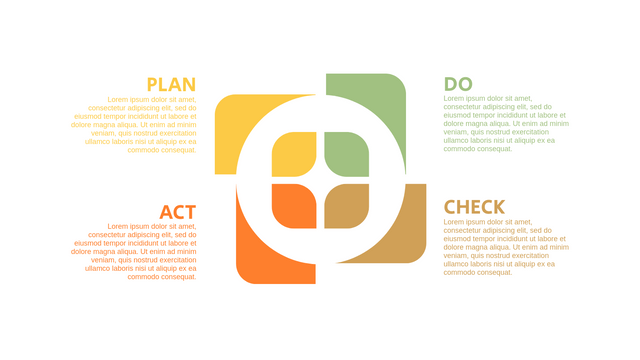
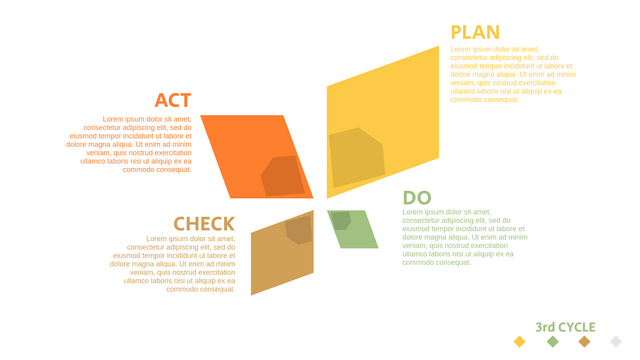
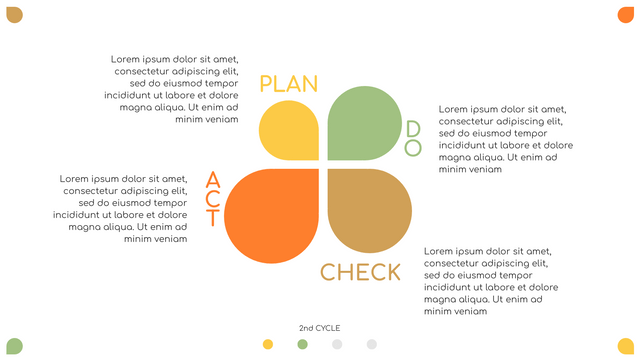
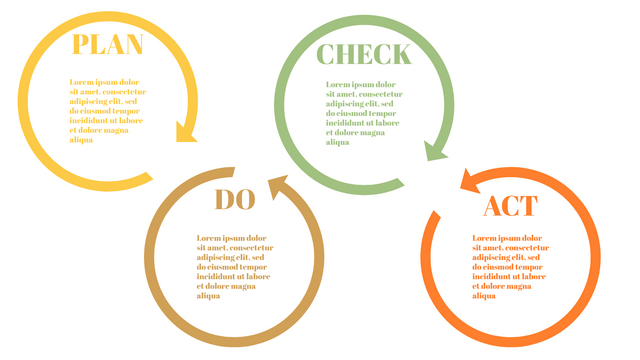
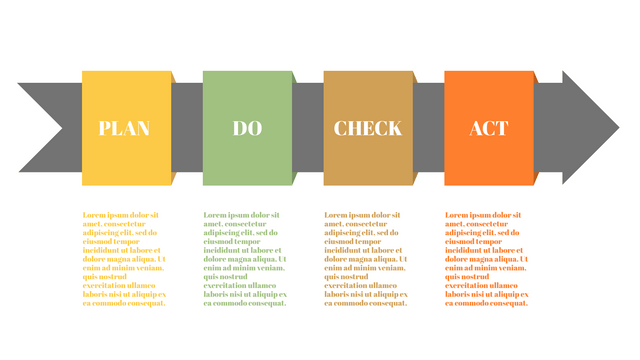
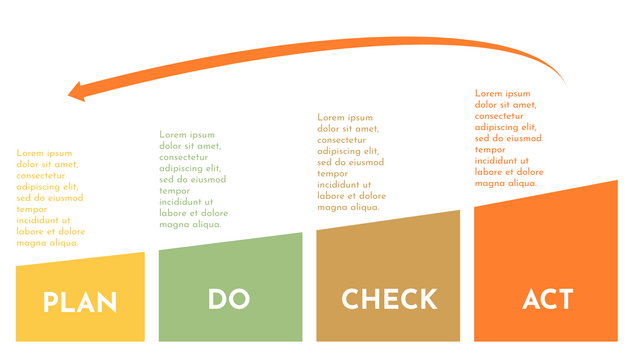
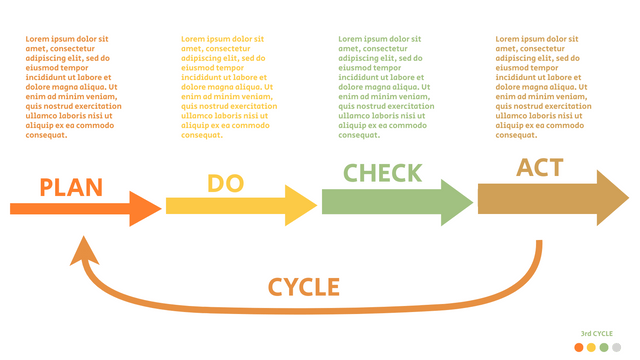
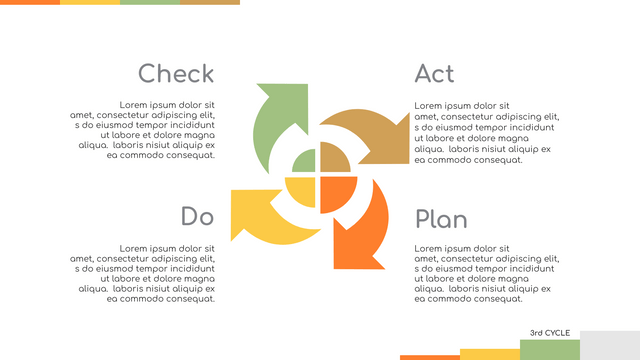
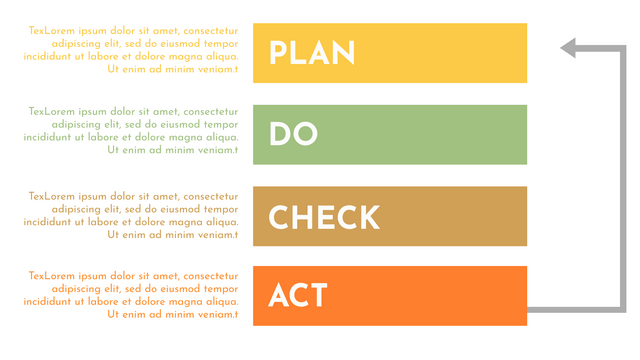
The PDCA cycle is a way to perform continuous improvement activities. It stands for Plan - Do - Check - Act known as the Deming cycle or the Shewhart cycle. The four steps of PDCA cycle (or Deming wheel) are:
Plan: identify and document opportunities; analyze existing problems; plan changes and steps you will take to address your findings and problems
Do: implement the solution (ideally on a small or controlled test bed). Write down your observations and findings
Check (Study): study what you find and observe during the "test" phase, and modify the steps as needed
Act (Action): implement or improve the process.
PDCA is also a never-ending cycle of improvement, rooted in the way a company or organization improves its products, services, or processes, which requires the long-term dedication and tolerance of those involved. PDCA is a difficult, often incremental process that can feel too slow and unbearable.