History of PDCA
Deming's theories form the basis of Total Quality Management (TQM) and ISO9001 quality standards. However, Demings himself credits Walter Andrew Shewhart as the creator of this cycle. Walter Andrew Shewhart was an American physicist, engineer, and statistician, often considered the father of statistical quality control.
What is PDCA Cycle?
The PDCA cycle, also known as the PDCA method, is a general model for optimizing quality management in enterprises. A loop provides a four-step problem-solving process. The purpose of long-term application of the PDCA cycle is to create a healthy foundation for internal quality management. The PDCA model can be traced back to the American physicist William Edwards Deming. His method is still regarded as an important pioneer in quality management.
4 Phases of PDCA Cycle
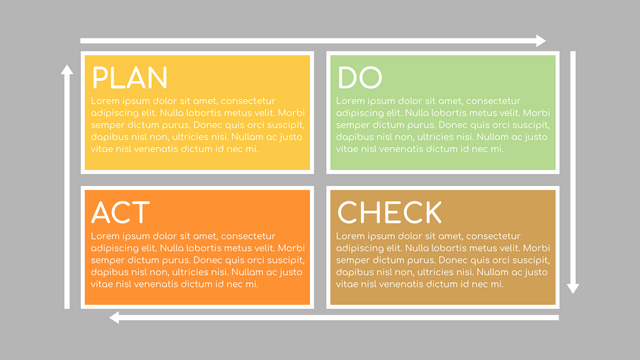
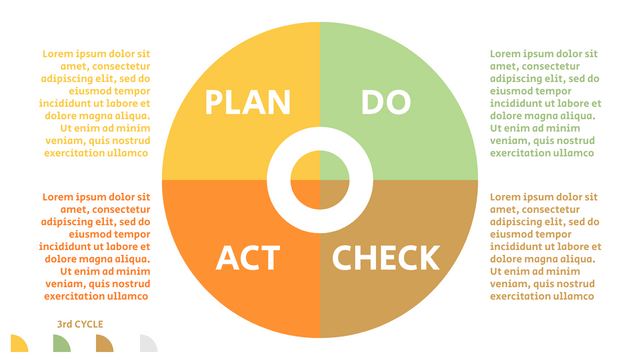
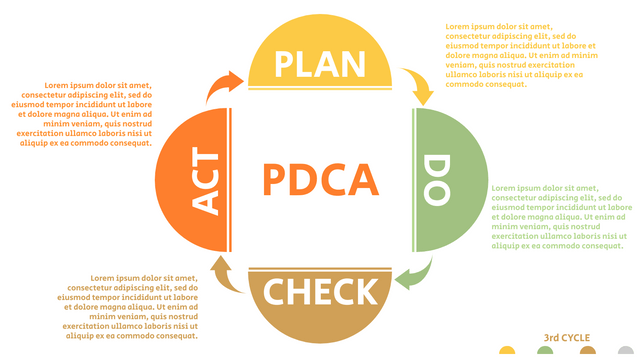
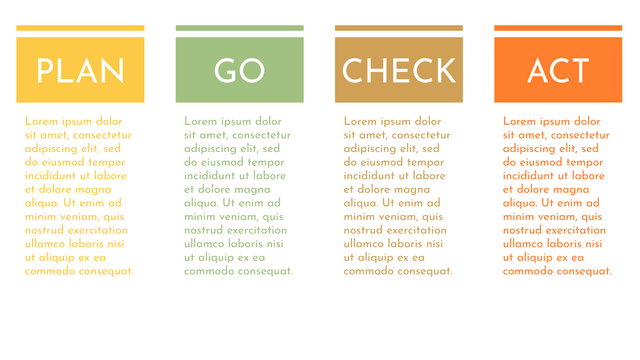
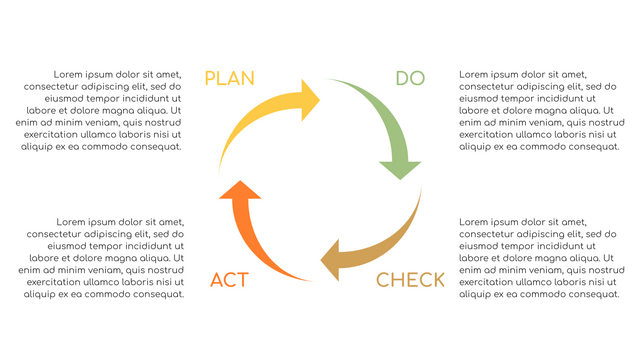
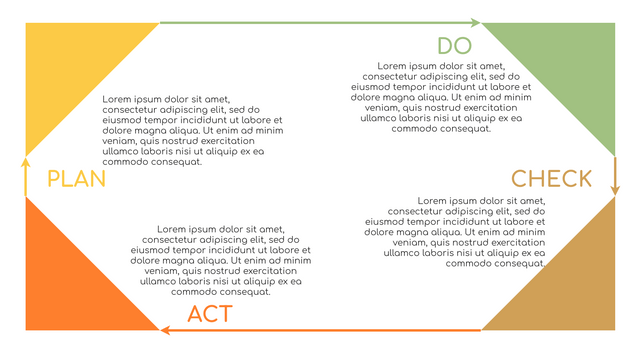
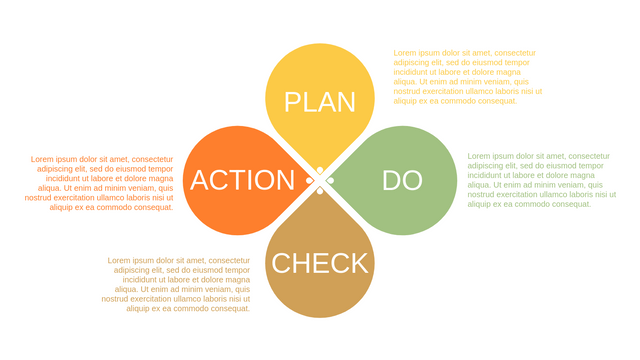
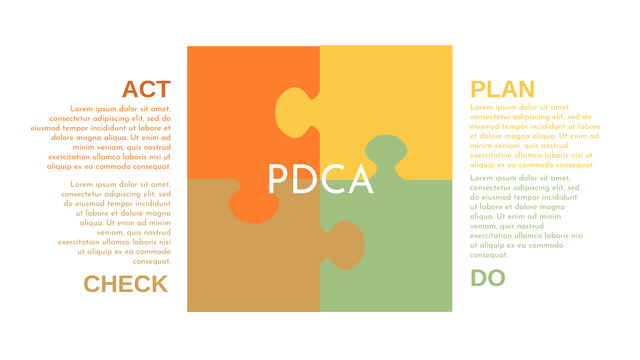
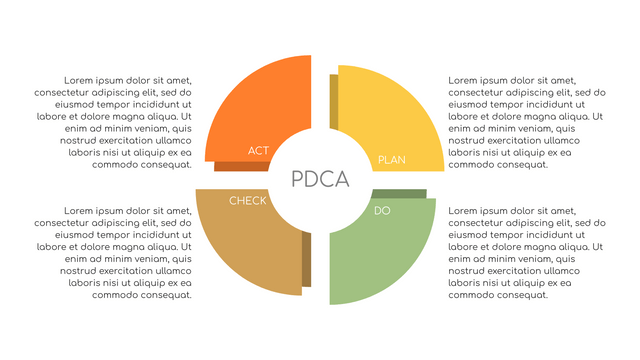
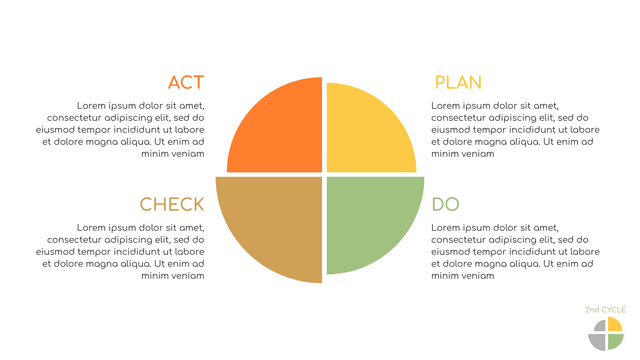
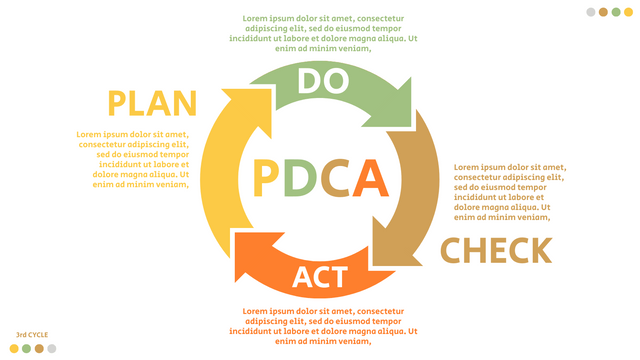
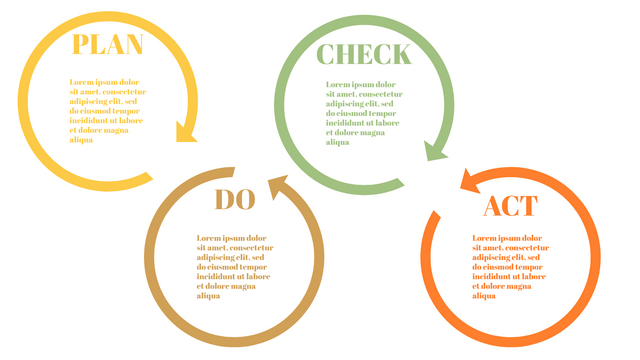
In the PDCA cycle, the whole process is divided into four phases, or steps. In this way, experts and managers can not only plan very precisely, but also conduct detailed success checks.
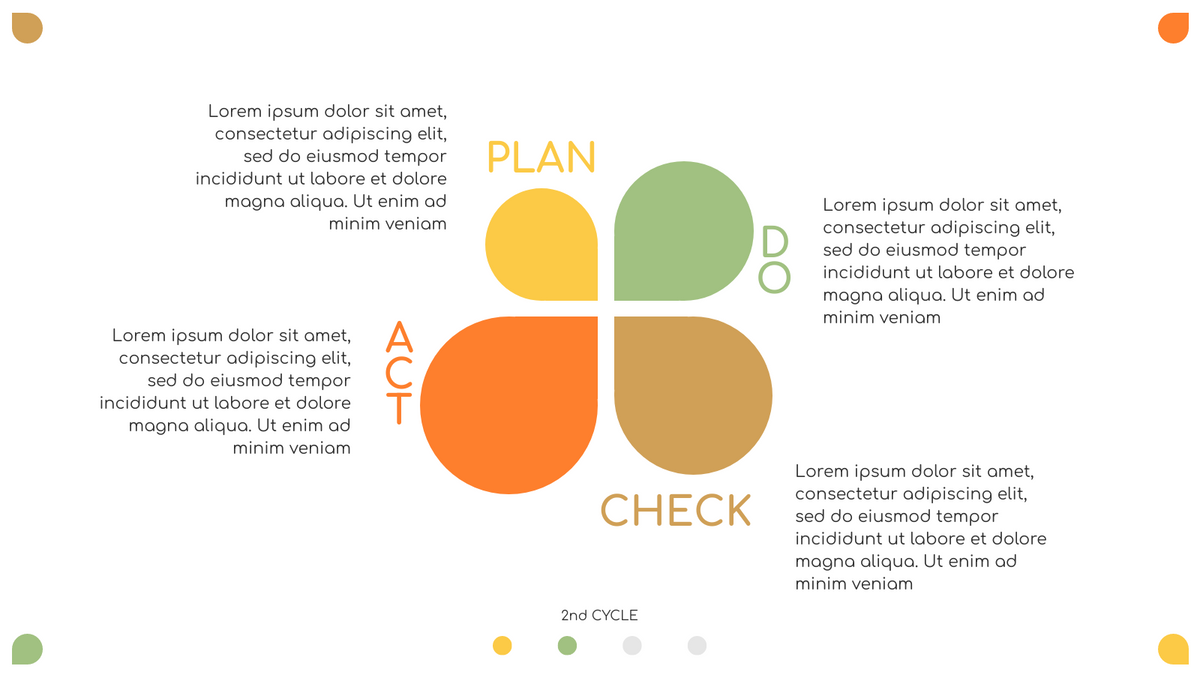
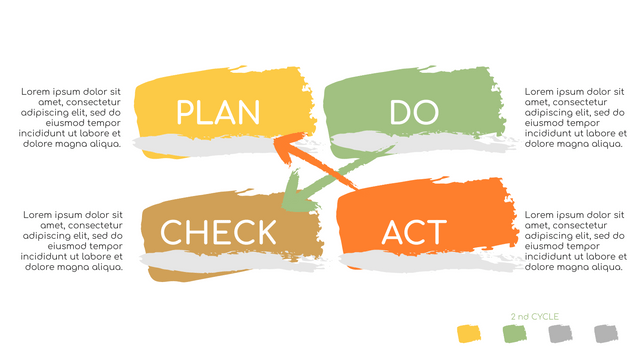
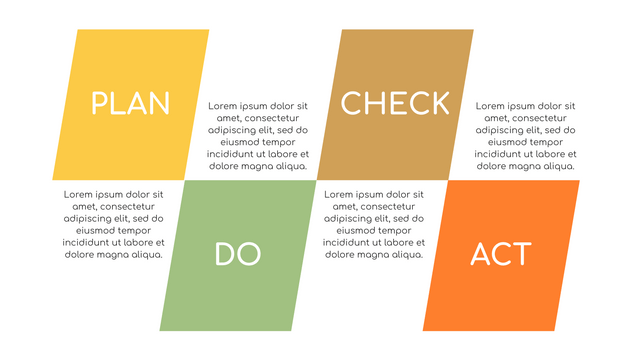
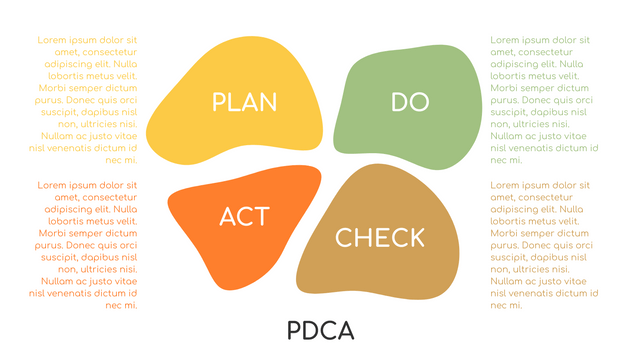
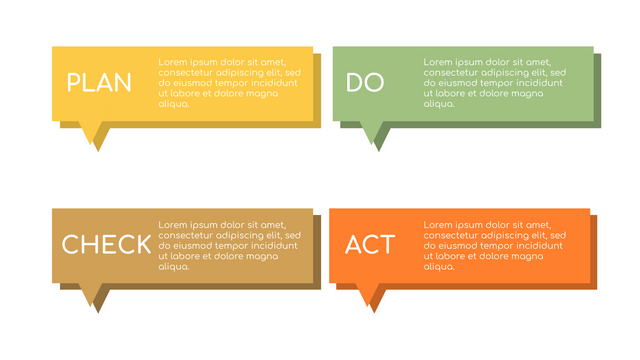
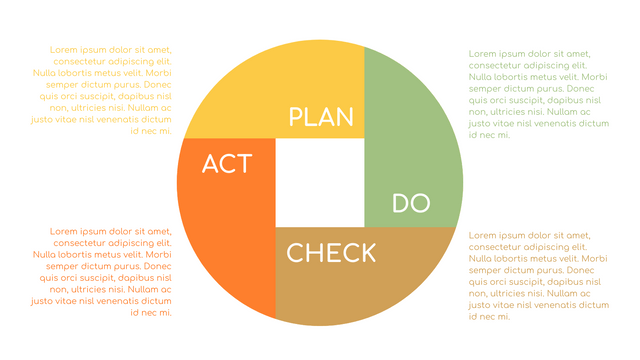
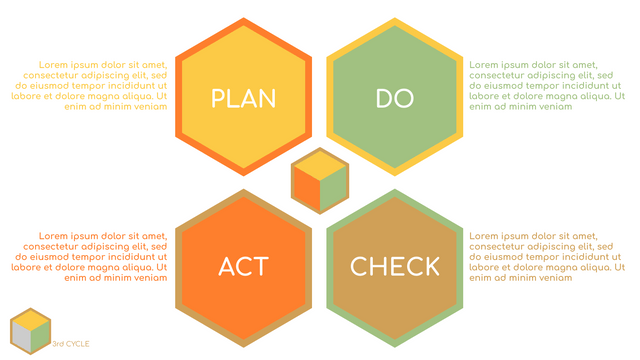
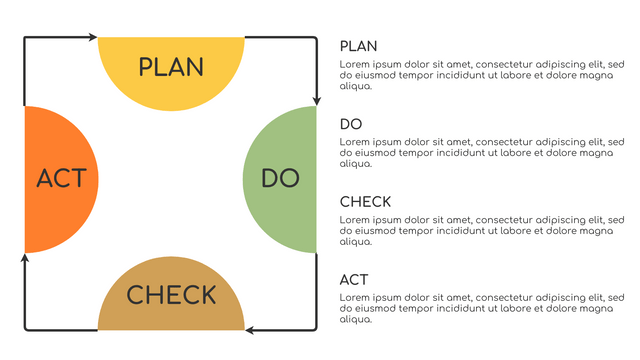
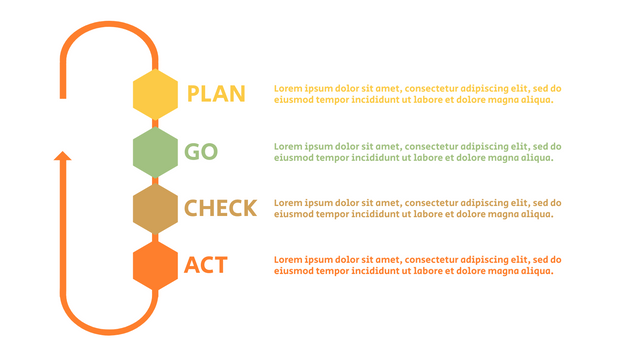
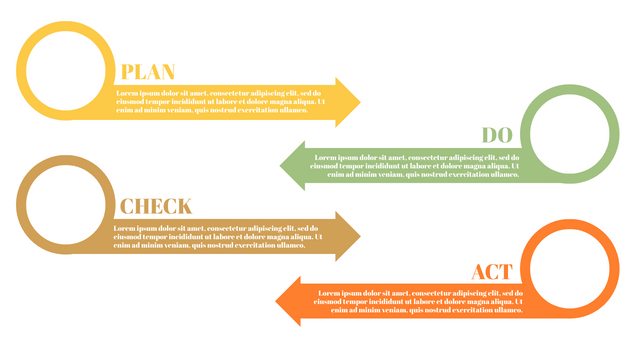
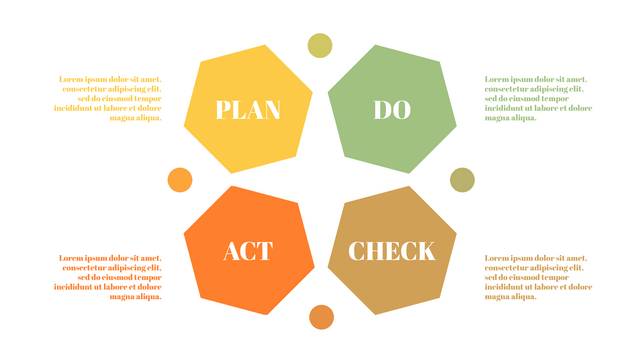
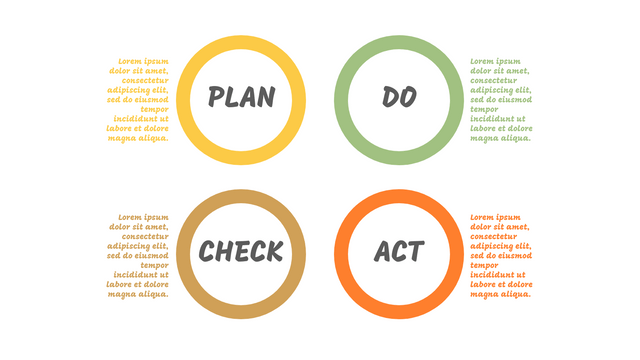
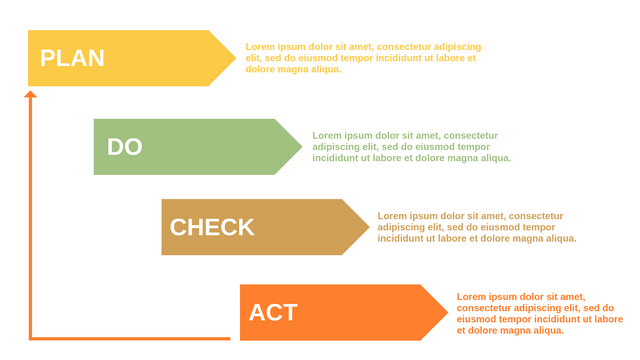
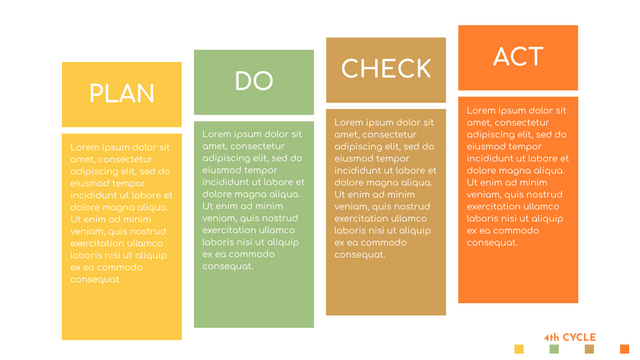
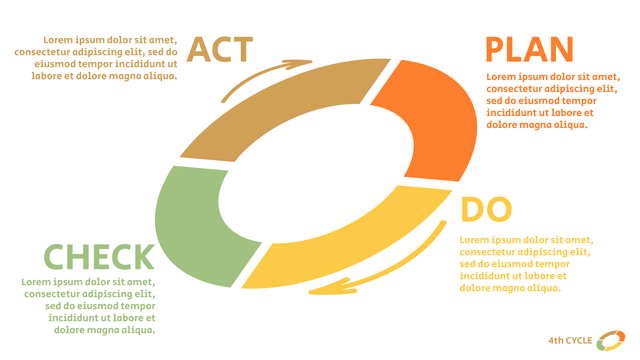
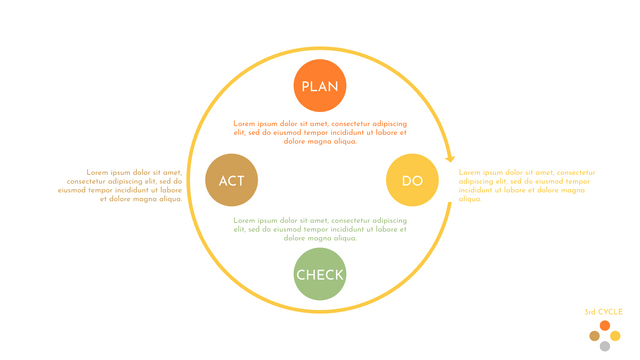
P (Plan): Identify the problem to be solved, collect relevant data, and determine the root cause of the problem.
D (Do): Develop and implement solutions; Decide how to measure its effectiveness.
C (Check): Confirm the results by comparing the data before and after.
A (Act): Record the results, inform others of the process changes, and make recommendations for issues to be addressed in the next PDCA cycle.
Application of PDCA in Lean Agile Method
PDCA is a valuable technique today that is part of the methodologies of Agile and Lean. Agile or not, this is an important aspect of successful project management. PDCA has been shown to improve productivity and performance while at the same time reducing project costs and the uncertainties involved with execution.