Originated in the 1980s by Michael Porter, value chain analysis is the conceptual notion of value-added in the form of a value chain. Value chain analysis is a way to visually analyze a company’s business activities to see how the company can create a competitive advantage for itself. Value chain analysis helps a company understand how it adds value to something and subsequently how it can sell its product or service for more than the cost of adding the value, thereby generating a profit margin. In other words, if they are run efficiently the value obtained should exceed the costs of running them i.e. customers should return to the organization and transact freely and willingly.
Michael Porter’s Value chain analysis is a process of dividing relevant activities of the business in primary and support activities that an organization performs to deliver something valuable, such as a product or service. Products pass through activities of a chain in order and, at each activity, the product gains some value. And to do so, inputs consumed by the activity and outputs generated are studied, to decrease costs and increase differentiation. Thus, a value chain framework helps organizations to identify the activities that are important for competitiveness.
Value chain analysis is used as a tool for identifying activities, within and around the firm and relating these activities to an assessment of competitive strength. Michael Porter classified the entire value chain into nine activities that are interrelated to one another. Porter suggested that an organization is split into ‘primary activities’ and ‘support activities’.
- Primary activities include the activities that are performed to satisfy external demand
- Secondary activities are those which are performed to satisfy internal requirements.
The figure below divides activities into primary and support activities as suggested by Porter’s Value Chain Analysis model:
Primary Activities: The functions which are directly concerned with the conversion of input into output and distribution activities are called primary activities. It includes:
- Inbound Logistics: Refers to goods being obtained from the organization’s suppliers and to be used for producing the end product.
- Operations: Raw materials and goods are manufactured into the final product. Value is added to the product at this stage as it moves through the production line.
- Outbound Logistics: Once the products have been manufactured they are ready to be distributed to distribution centers, wholesalers, retailers or customers. Distribution of finished goods is known as outbound logistics.
- Marketing and Sales: Marketing must make sure that the product is targeted towards the correct customer group. The marketing mix is used to establish an effective strategy, any competitive advantage is communicated to the target group through the promotional mix.
- Service: After the product/service has been sold what support services do the organization offer customers? This may come in the form of after-sales training, guarantees, and warranties.
Support Activities: Those activities which assist primary activities in accomplishment, support activities. These are:
- Procurement: This department must source raw materials for the business and obtain the best price for doing so. The challenge for procurement is to obtain the best possible quality available (on the market) for their budget.
- Technology Development: The use of technology to obtain a competitive advantage is very important in today’s technology-driven environment. Technology can be used in many ways including production to reduce cost thus add value, research, and development to develop new products and the internet so customers have 24/7 access to the firm.
- Human Resource Management: The organization will have to recruit, train and develop the correct people for the organization to be successful. Staff will have to be motivated and paid the ‘market rate’ if they are to stay with the organization and add value. Within the service sector such as the airline industry, employees are the competitive advantage as customers are purchasing a service, which is provided by employees; there isn’t a product for the customer to take away with them.
- Infrastructure: Every organization needs to ensure that its finances, legal structure, and management structure work efficiently and helps drive the organization forward. Inefficient infrastructures waste resources, could affect the firm’s reputation and even leave it open to fines and sanctions.
In the fast-paced world, the main focus of the organization is customer satisfaction, and value chain analysis is the technique that helps to attain that level. Under this, each business activity is considered as essential, which contributes value and is constantly analyzed, to increase value as regards the cost incurred.
The Link between Primary and Support Activities
As mentioned before, primary activities add value directly to the production process, but they are not necessarily more important than support activities. Nowadays, competitive advantage mainly derives from technological improvements or innovations in business models or processes. Therefore, such support activities as ‘information systems’, ‘R&D’ or ‘general management’ are usually the most important source of differentiation advantage. On the other hand, primary activities are usually the source of cost advantage, where costs can be easily identified for each activity and properly managed.
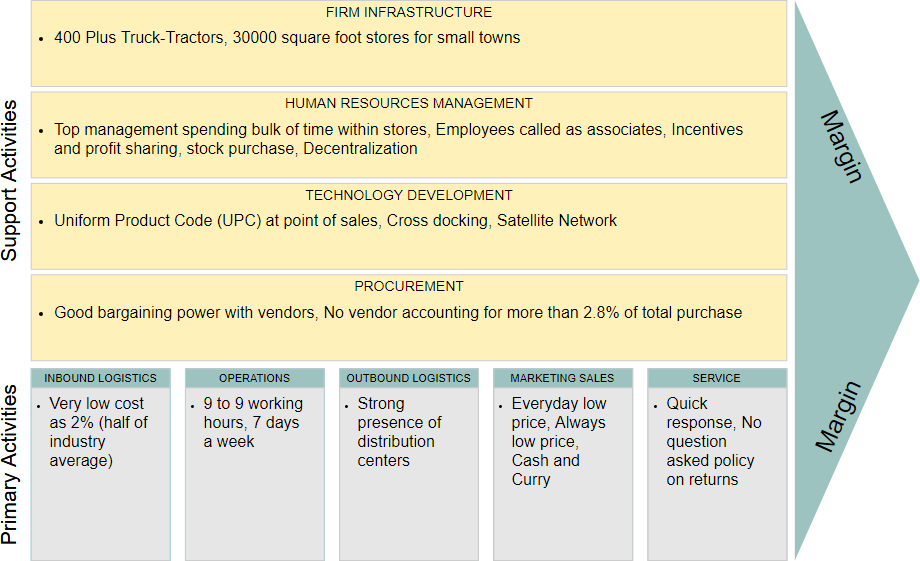
Value Chain Diagram Example – WalMart’s Value Chain Analysis
There are 2485 Wal-Mart stores all over the world. This includes 682 Supercenters, 457 Sam’s Clubs, 5 Wal-Mart Neighborhood Markets and 1007 units of Wal-Mart International. Wal-Mart serves over 100 million customers weekly worldwide. There are 1035000 associates, and the company is America’s largest private employer.
- Wal-Mart is run from a national headquarter. The headquarter takes care of orders, and every local store has to report to the Head Quarter. The local store is responsible for satisfying the local customer.
- Every associate is challenged to reduce the cost of doing business, ranging from reduced paper use to make suggestions that can save millions of dollars. This challenge is met every day because associates understand that the savings they create are passed to the customer at low prices.
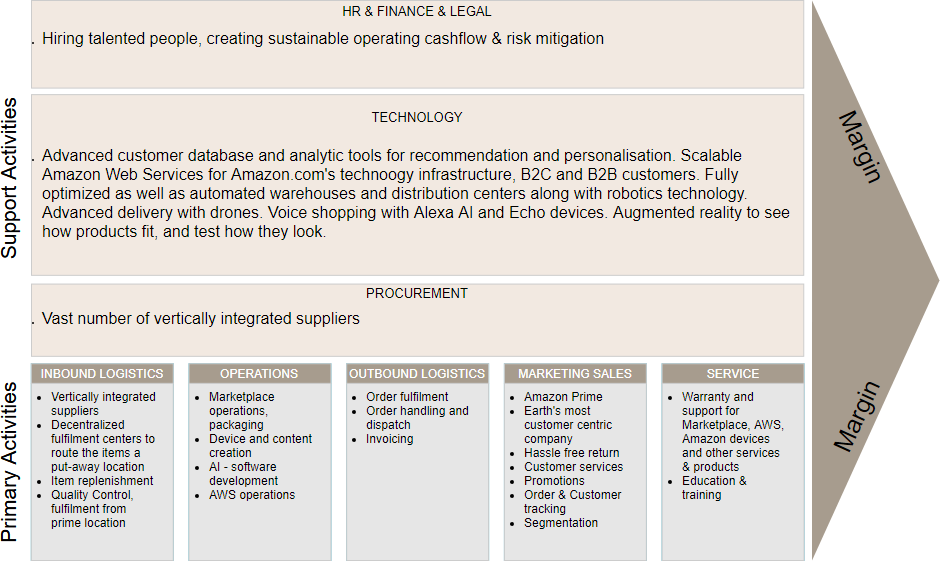
Value Chain Analysis Example – Amazon
- com, Inc. founded in 1994 by Jeff Bezos.
- American electronic commerce company with headquarters in Seattle, Washington.
- Started as an online bookstore and diversified to selling DVDs, CDs, electronics, apparel, furniture, toys, and jewelry.
- Serving in 7 countries, 21 fulfillment centers and globally more than 9 million square feet of warehouse space.
Perform Value Chain Analysis Online
A Value Chain Diagram is a visual representation of a value chain, which is a set of activities that a business performs to deliverable a valuable product or service for the market. Visual Paradigm Online features a Value Chain Diagram software that makes drawing Value Chain Diagram easy with the help of easy bullet editor and auto-layout facility! You just need to enter the primary activities and support activities, then the Value Chain Diagram will be formed automatically. No manual work, no distorted graphics! Of course, you can always adjust the height, color or other look & feel of the InfoArt, if you wish to.