PDCA is a pattern that assists in the control and continuous improvement of processes and projects. Japan began to apply it in lean manufacturing from the 1950s, its circular method through continuous iteration and incremental gain of experience, so as to constantly update the work process, and finally get a more efficient business process.
PDCA was popularized by W. Edwards-Deming, a leader in modern quality control processes and procedures. Deming intends to use PDCA when developing new or improved processes, products or services, implementing changes, or defining repetitive work processes.
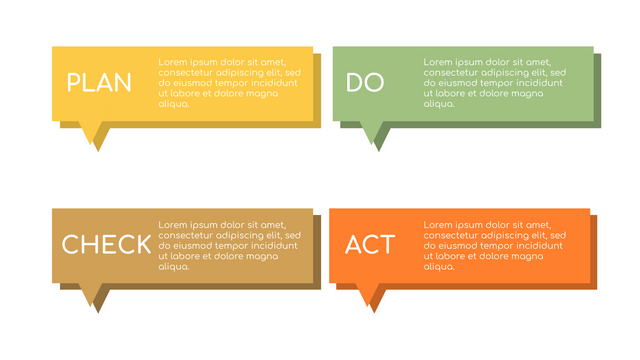
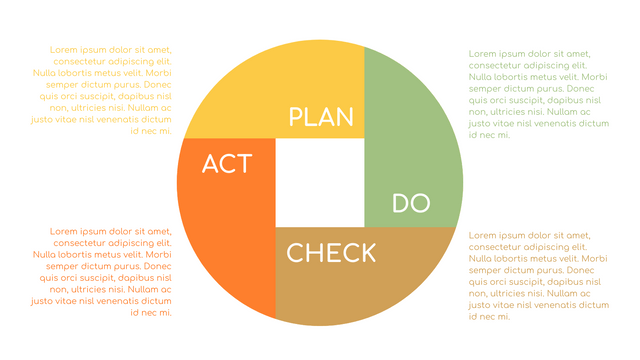
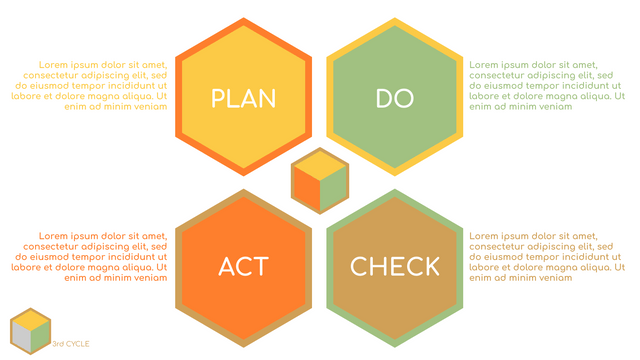
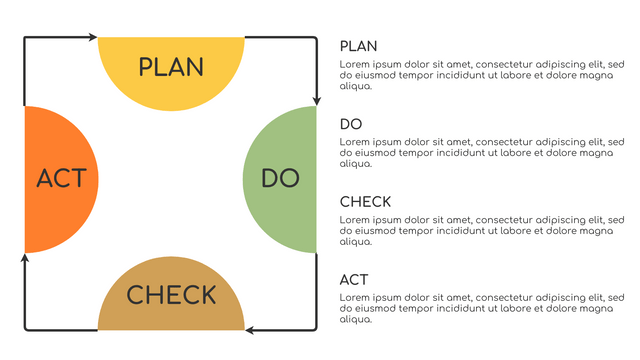
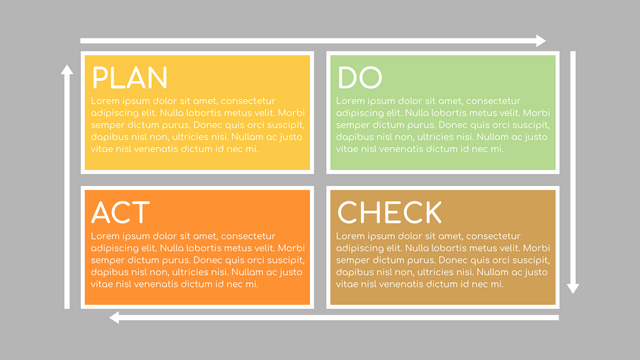
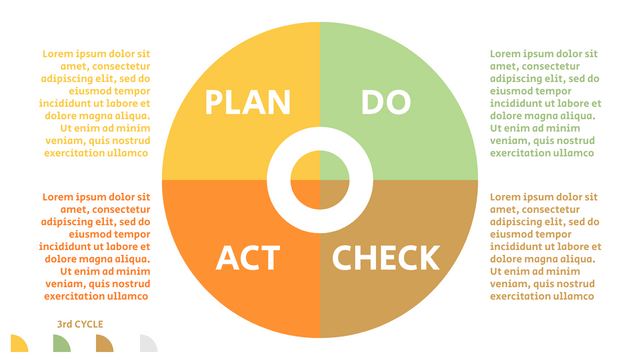
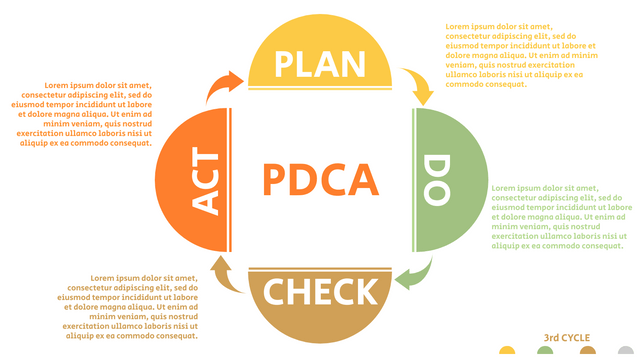
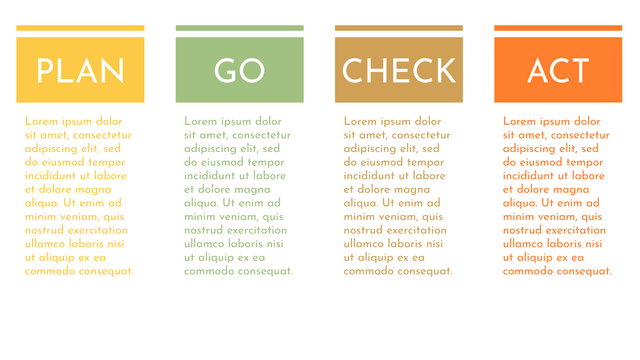
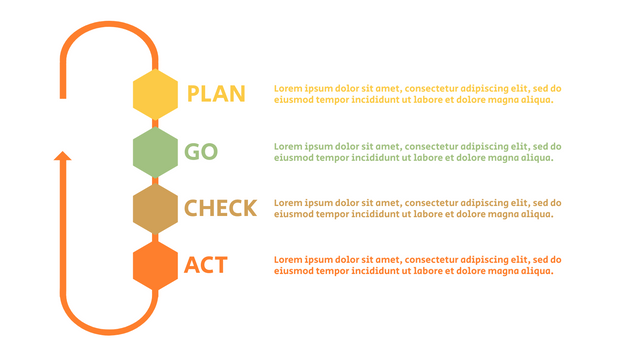
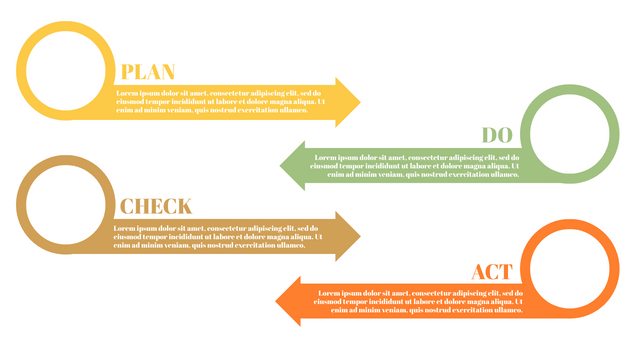
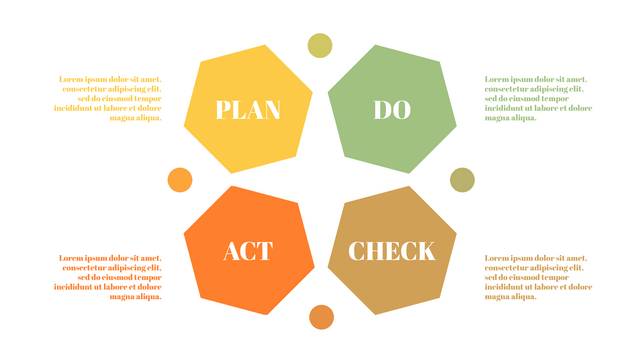
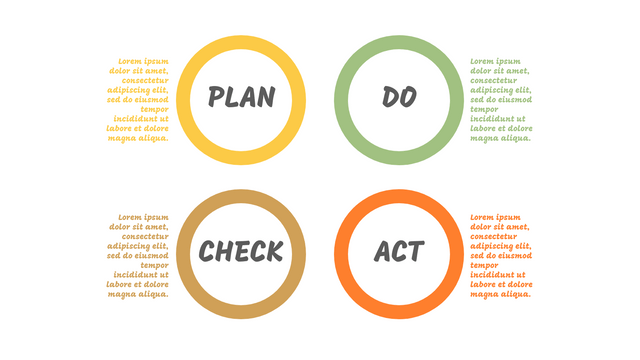
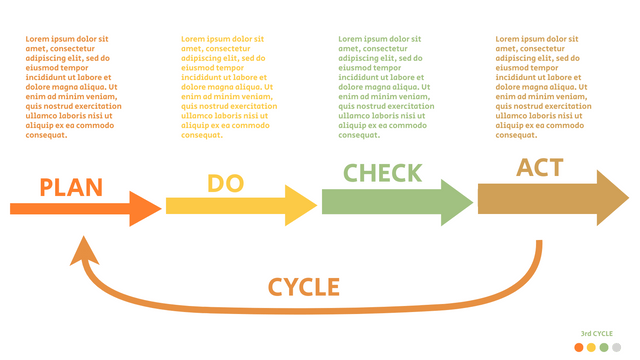
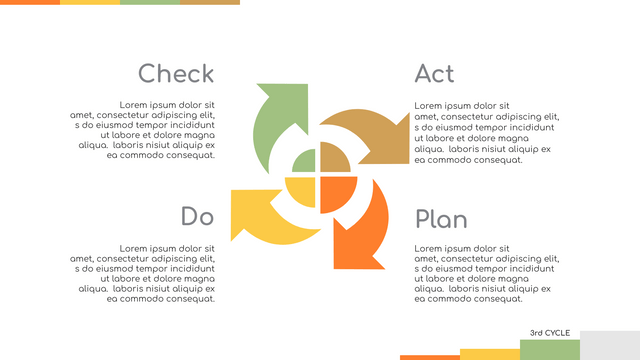
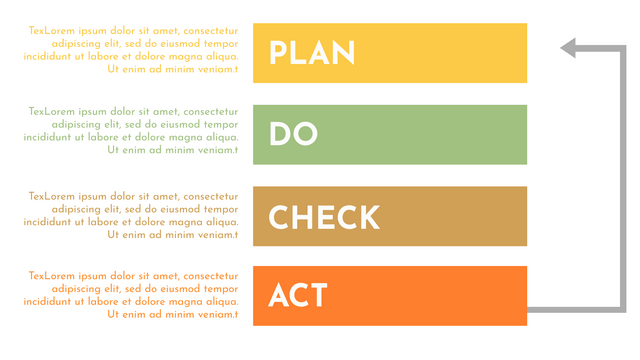
It consists of four stages:
Plan: Assess current or new processes and how to improve.
Do: Test small changes to assess their effectiveness as part of a pilot project.
Check: Collect and analyze test results, compare them with expected results, and determine what has been learned.
Act: Take action based on the lessons learned in the "check" steps.
The periodicity of PDCA impels the organization to improve the process or product to get closer to the ideal state. Its simplicity makes the process easier to follow and makes it suitable for various business situations.