PMI Chart (the letters stand for plus, minus, interesting) is a brainstorming, decision making and critical thinking tool which can be a useful method of analyzing and reaching agreed understandings on complex issues and make a more balanced decision. It is used to encourage the examination of ideas, concepts, and experiences from more than one perspective.
A PMI strategy can help you to:
- Brainstorm ideas by encouraging the members of the group to look at a proposed idea from multiple viewpoints, rather than taking a side and holding their ground.
- Provides a broader view of the group’s views on the topic.
- identify strengths and weaknesses for a problem for future improvement
- make decisions quickly by analyzing and weighing the pros and cons
What is PMI Chart?
PMI was developed by Dr. Edward de Bono, a proponent of lateral and critical thinking. Learners can use the chart in discussion activities. A PMI Chart is useful in a debate over a difficult decision because these types of decisions bring up many plusses and minuses. However, views and ideas will likely arise which don’t classify as either a plus or a minus, and these would be placed in the interesting column. Its power isn’t in the information itself, but the discussion that arises from the entries in the columns.
4 Steps for Creating PMI Chart
To complete you make a chart of three columns – “Plus”, “Minus” and “Interesting.”
- Considering the Positive points of a Situation – identify all of the positive things you can think of. Don’t critique yourself along the way, simply spill out all the positive points that you can think of.
- Considering the minus points of a Situation – identify all of the negative things you can think of. Again, don’t critique yourself. Simply spill out all the negative points you can think of.
- Considering the Interesting Points of a Situation – identify all the interesting points that you can think of. Rather than positive or negative, they are simply points of interest that you should direct your attention to.
- Making a Balanced Decision – make balanced decisions because you’ve reviewed and organized three important perspectives of the situation: the positives, the negatives, and the interesting.
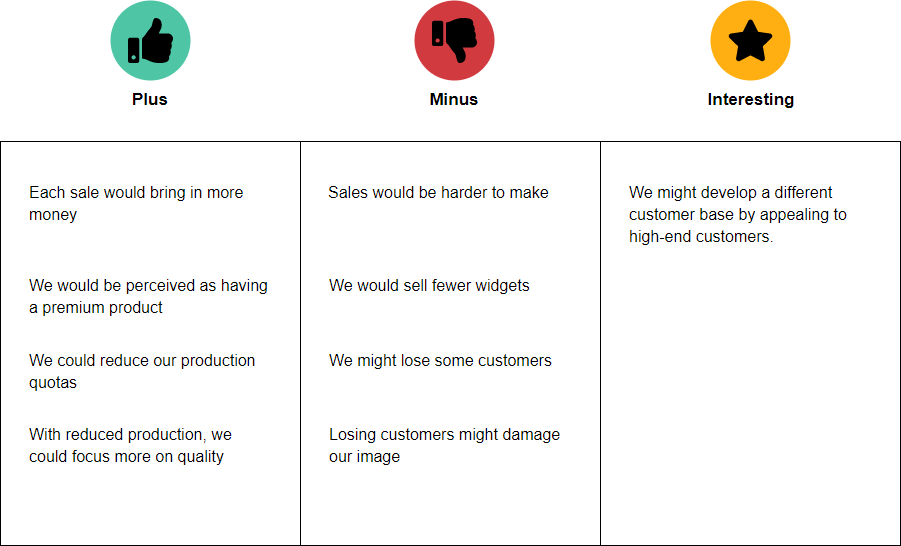
Example: Increase Product Price