The purpose of any management system is to make the company know its actual performance, and then can effectively take action to improve. In fact, we can implement improvements by correctly understanding and leveraging the Plan-Do-Check-Action (PDCA) cycle. This means that the company must establish efficient and effective procedures (Plans), implement these "plans" (Do), monitor the resulting data (Check), and take appropriate actions to improve, correct, and prevent problems (Act).
When to Use PDCA Cycle?
The PDCA method has been adopted by many international standards, including BS25999 and NFPA1600 (2010 edition), and has been adopted by many industries. While PDCA can improve almost any business process, it is particularly useful in the following use cases:
Start a new project, with many repetitive and routine tasks
Implement total quality management, lean manufacturing, agile approach or six sigma approach
Develop new or improved designs for products, services, or processes
What is PDCA?
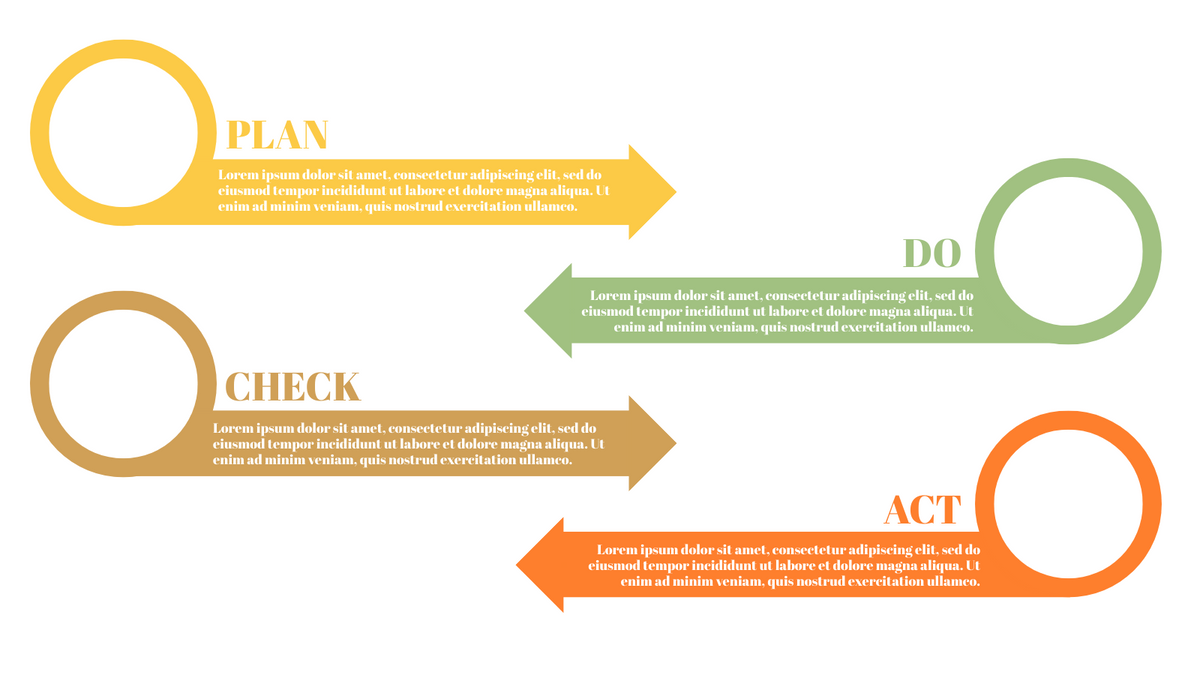
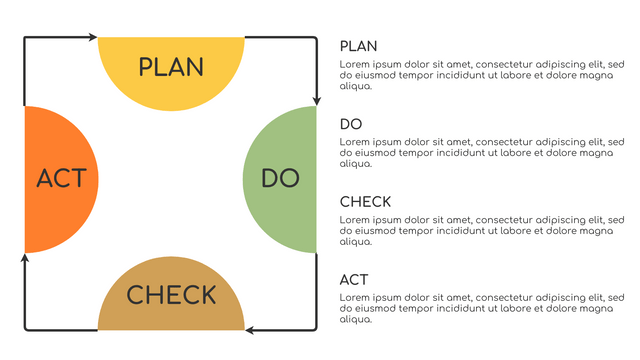
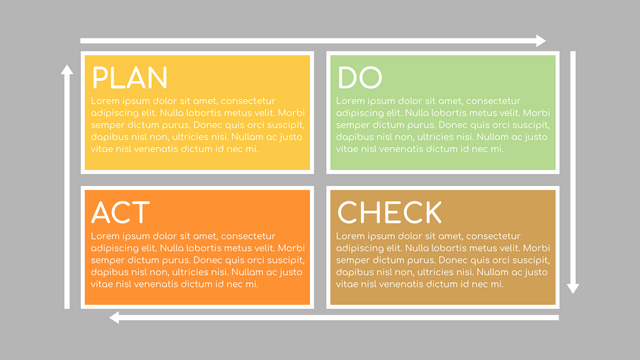
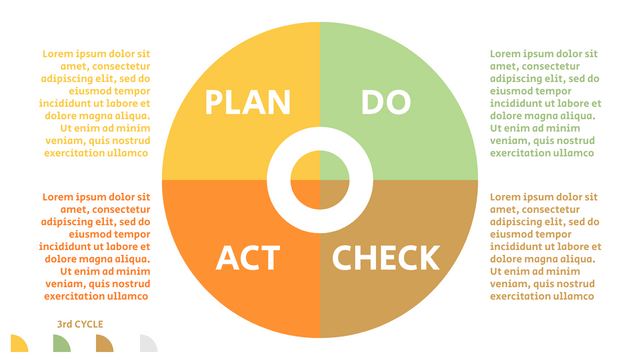
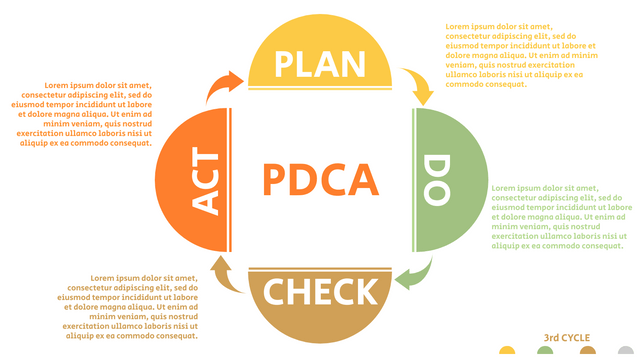
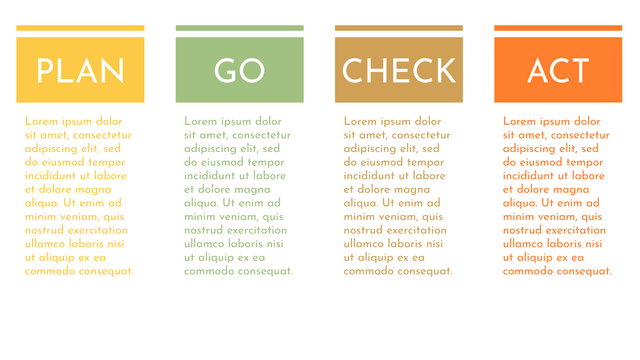
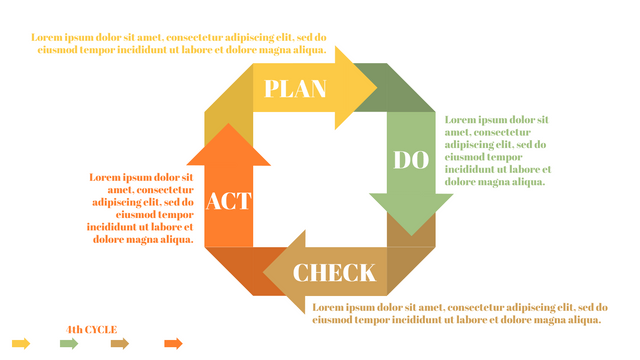
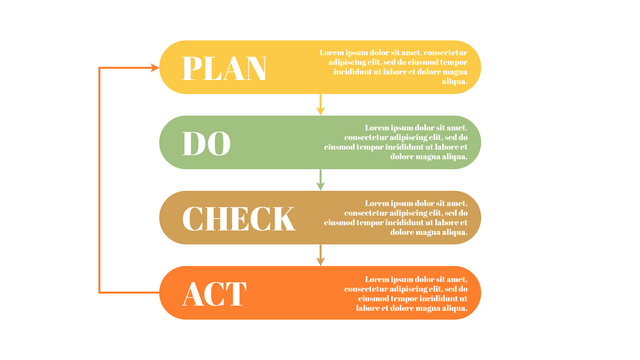
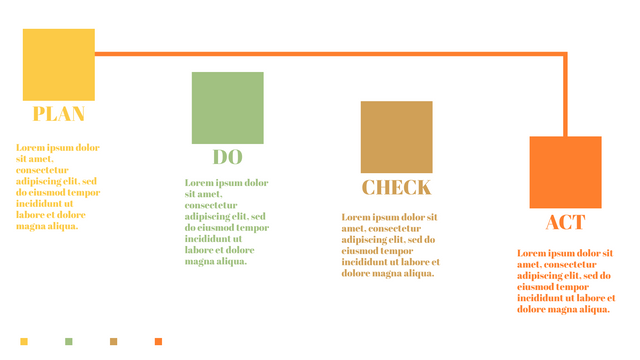
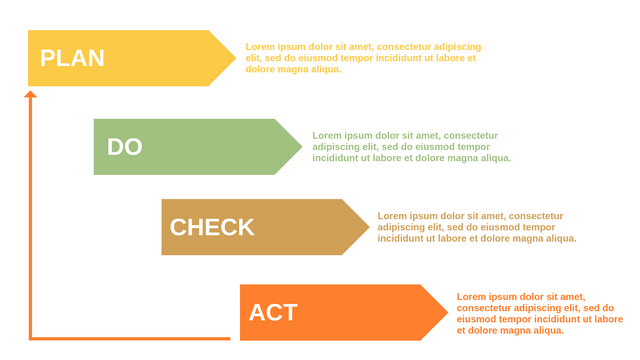
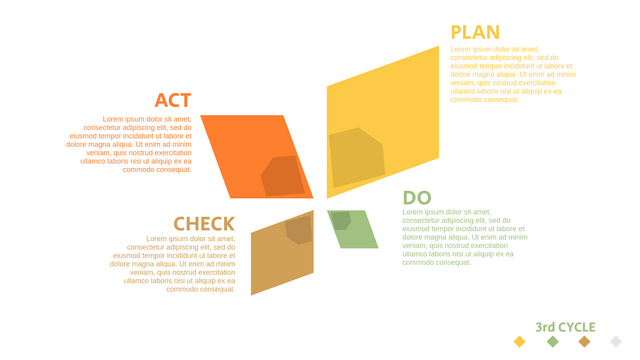
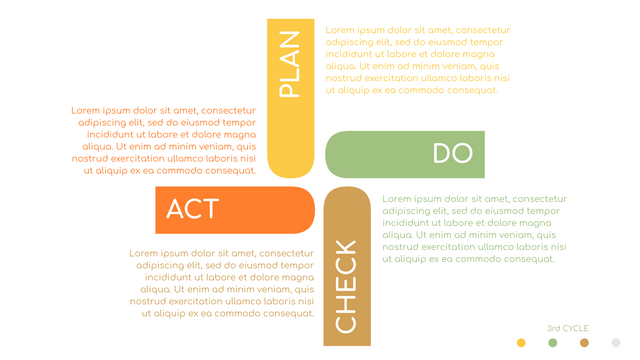
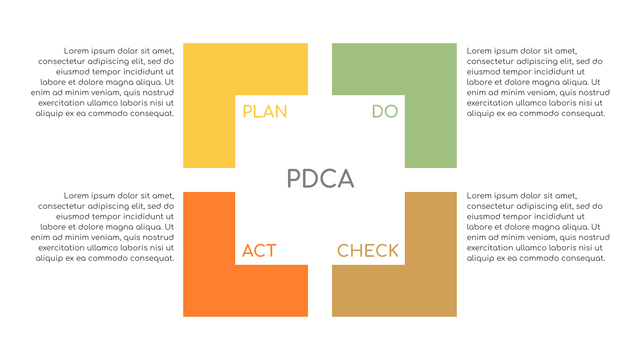
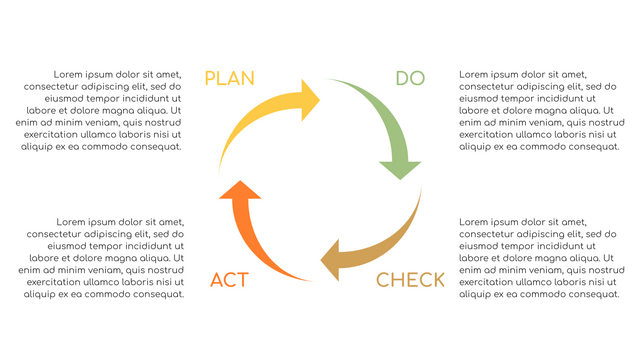
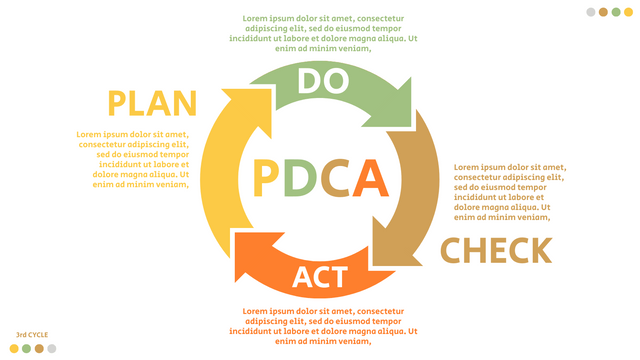
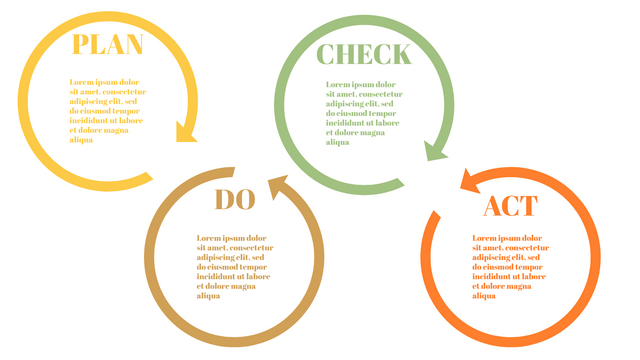
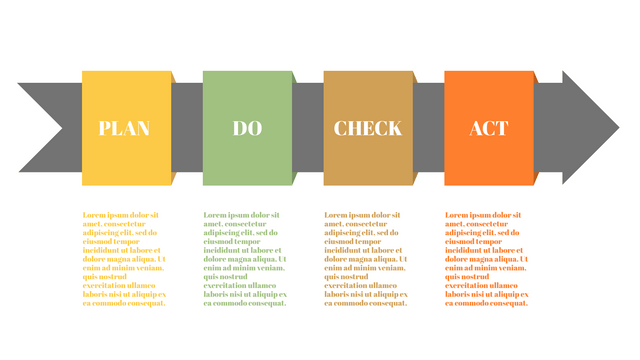
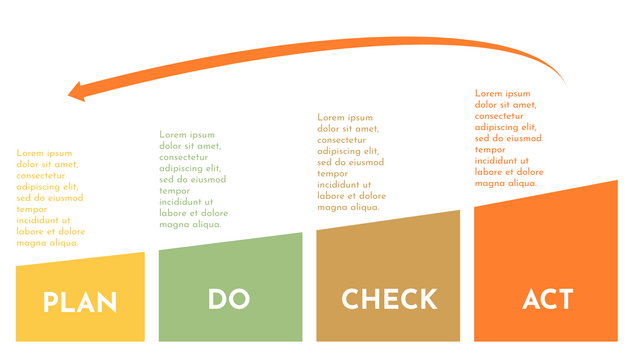
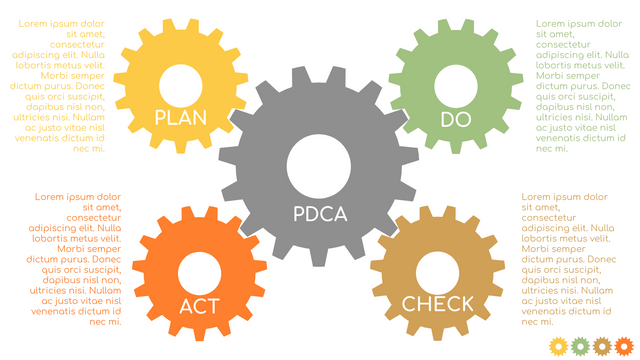
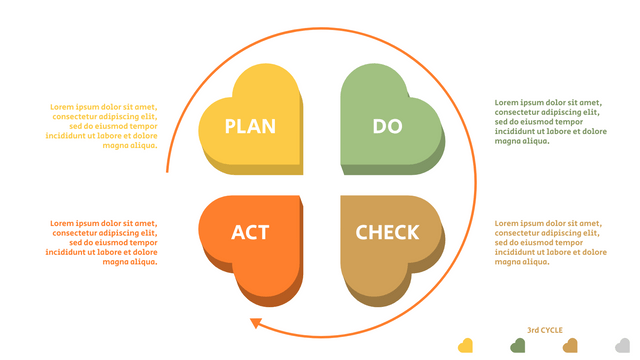
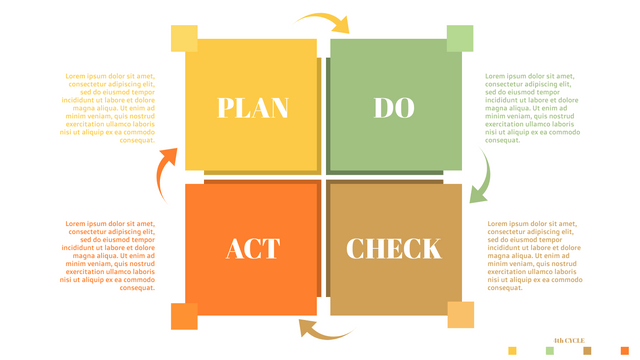
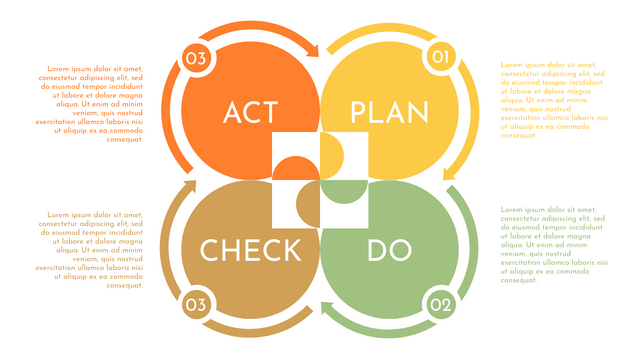
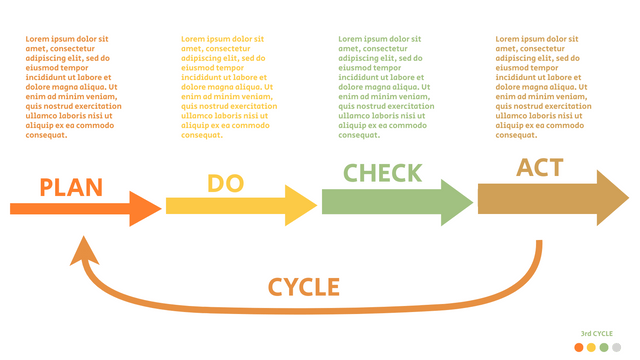
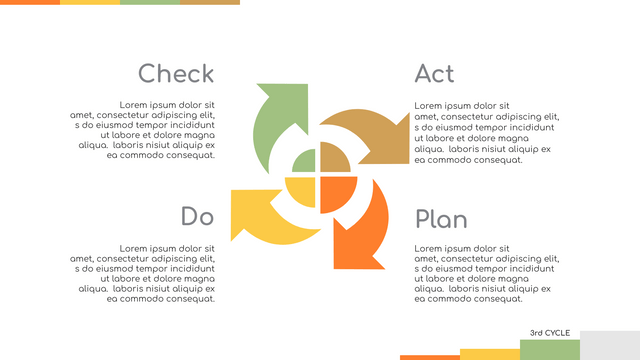
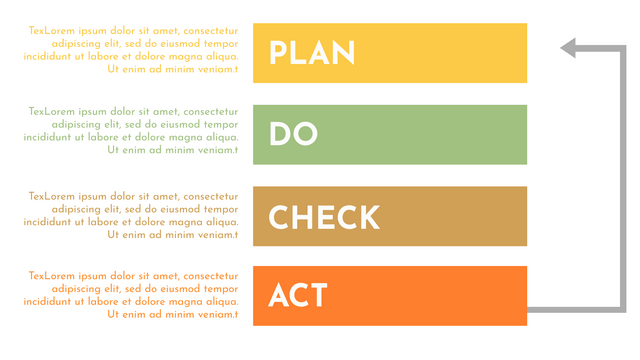
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, also known as plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA), Deming Wheel or Deming cycle, is a continuous four step cycle quality tool for improvement and change. This systematic approach helps companies think about what needs to be changed and then test it in a continuous feedback loop to solve the problem. The four stages are:
Plan: identify and analyze problems or opportunities, make assumptions about which methods can be changed and completed, and decide which assumptions to test.
Do: test selected assumptions, preferably on a small scale, and measure results.
Check: the results of the study, measuring the effectiveness of the changes made, and determining whether they support the hypothesis.
Act: if the solution is successful, implement it throughout the process.