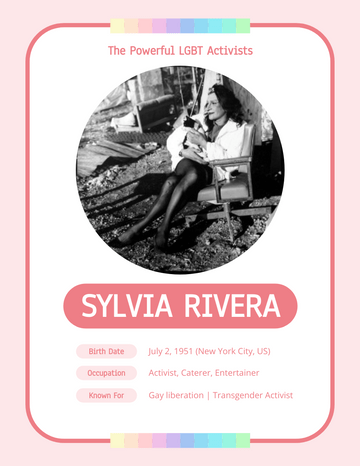
THE GREAT EXPLORER
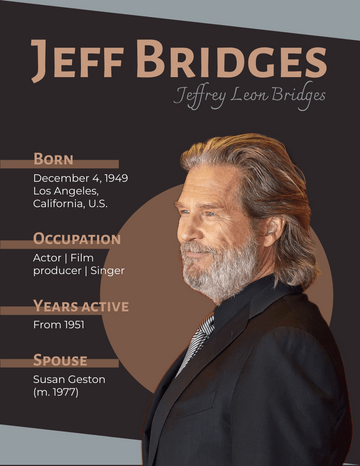
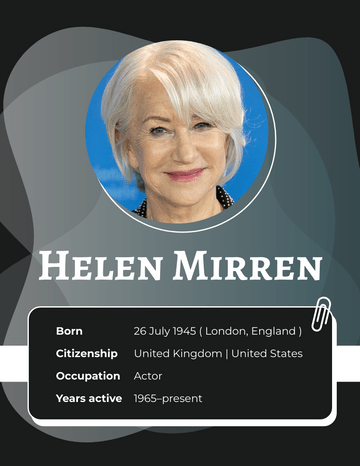
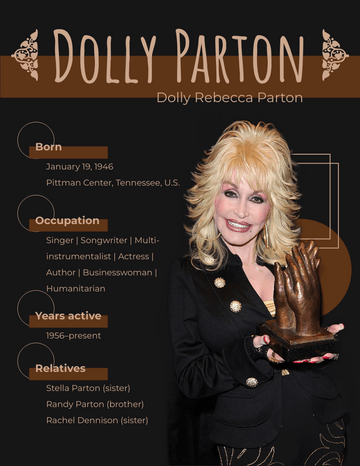
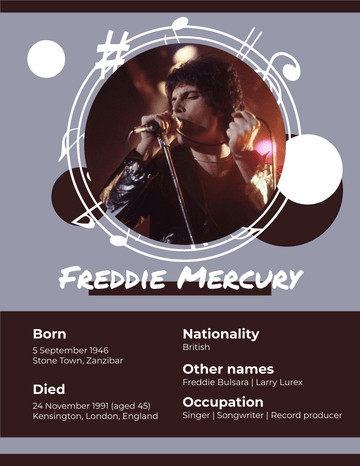
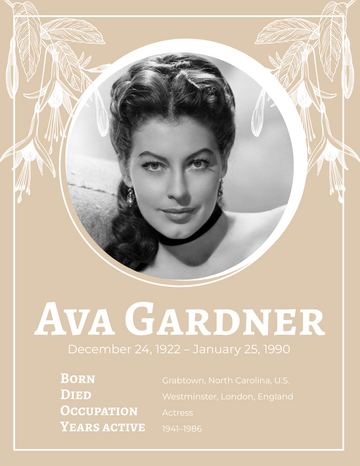
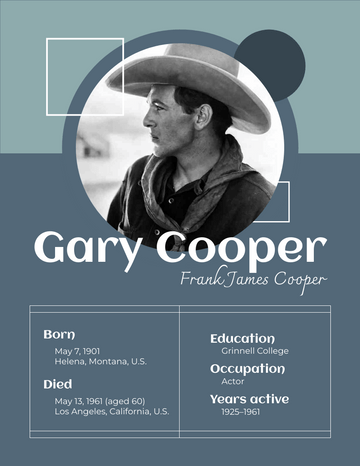
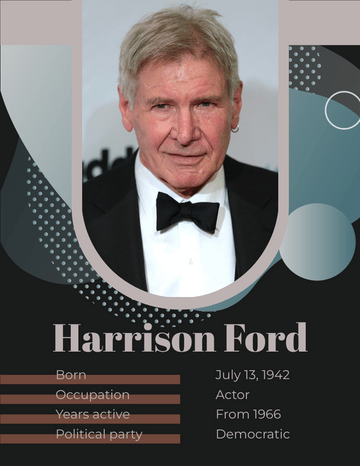
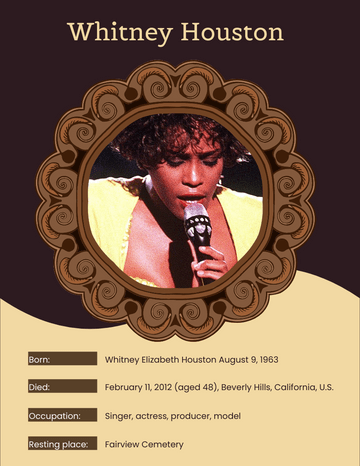
Ernest Hemingway
Birth Date July 21, 1899
Notable works The Sun Also Rises A Farewell to Arms
For Whom the Bell Tolls The Old Man and the Sea
Notable awards Pulitzer Prize for Fiction (1953) | Nobel Prize in Literature (1954)
Click here to read this biography book.
Who is Ernest Hemingway
Ernest Miller Hemingway (July 21, 1899 – July 2, 1961) was an American novelist, short-story writer, and journalist. His economical and understated style—which he termed the iceberg theory—had a strong influence on 20th- century fiction, while his adventurous lifestyle and public image brought him admiration from later generations. Hemingway produced most of his work between the mid-1920s and the mid-1950s, and he was awarded the 1954 Nobel Prize in Literature. He published seven novels, six short-story collections, and two nonfiction works. Three of his novels, four short-story collections, and three nonfiction works were published posthumously. Many of his works are considered classics of American literature. Hemingway was raised in Oak Park, Illinois. After high school, he was a reporter for a few months for The Kansas City Star before leaving for the Italian Front to enlist as an ambulance driver in World War I. In 1918, he was seriously wounded and returned home. His wartime experiences formed the basis for his novel A Farewell to Arms (1929).
His Early Life
Ernest Miller Hemingway was born on July 21, 1899, in Oak Park, Illinois, an affluent suburb just west of Chicago, to Clarence Edmonds Hemingway, a physician, and Grace Hall Hemingway, a musician. His parents were well- educated and well-respected in Oak Park, a conservative community about which resident Frank Lloyd Wright said, "So many churches for so many good people to go to." When Clarence and Grace Hemingway married in 1896, they lived with Grace's father, Ernest Miller Hall, after whom they named their first son, the second of their six children. His sister Marcelline preceded him in 1898, followed by Ursula in 1902, Madelaine in 1904, Carol in 1911, and Leicester in 1915. Grace followed the Victorian convention of not differentiating children's clothing by gender. With only a year separating the two, Ernest and Marcelline resembled one-another strongly. Grace wanted them to appear as twins, so in Ernest's first three years she kept his hair long and dressed both children in similarly frilly feminine clothing.