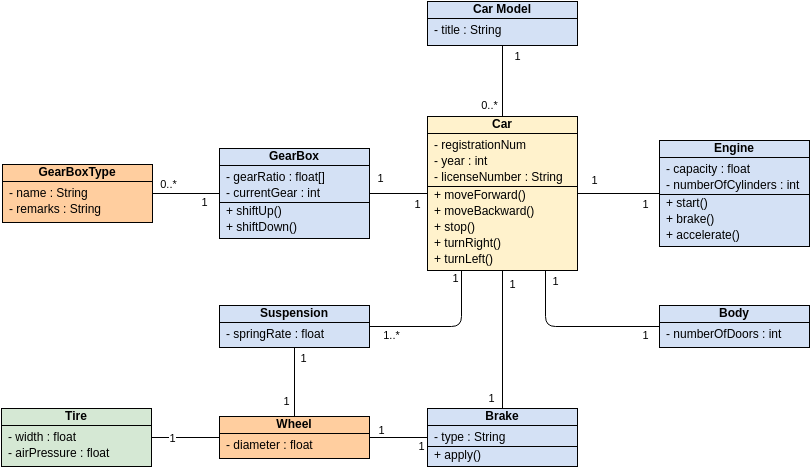
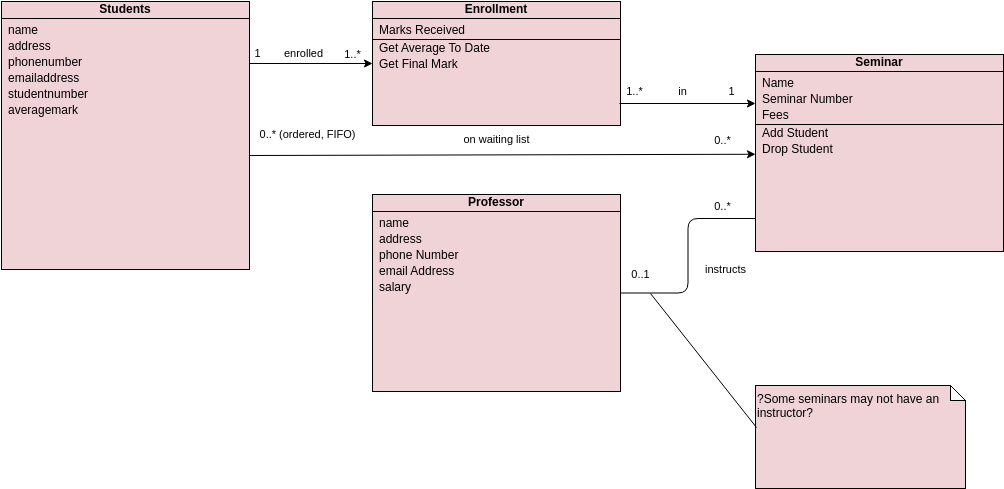
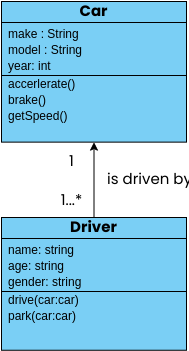
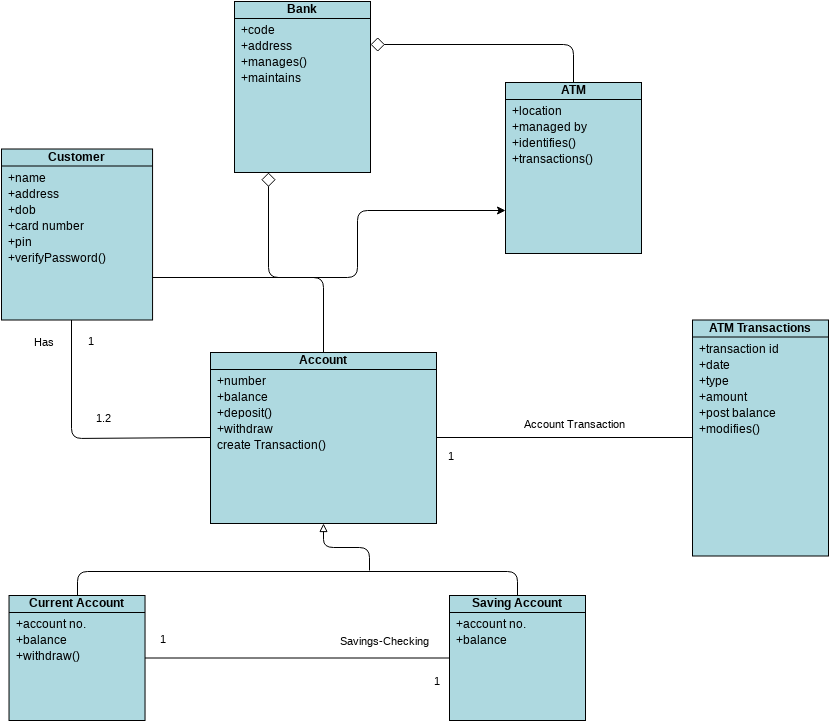
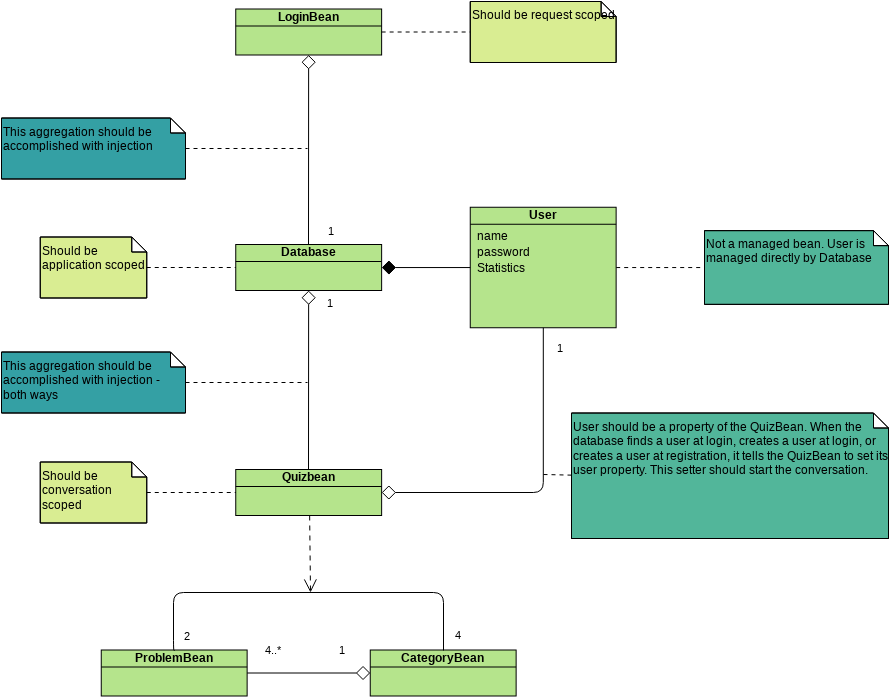
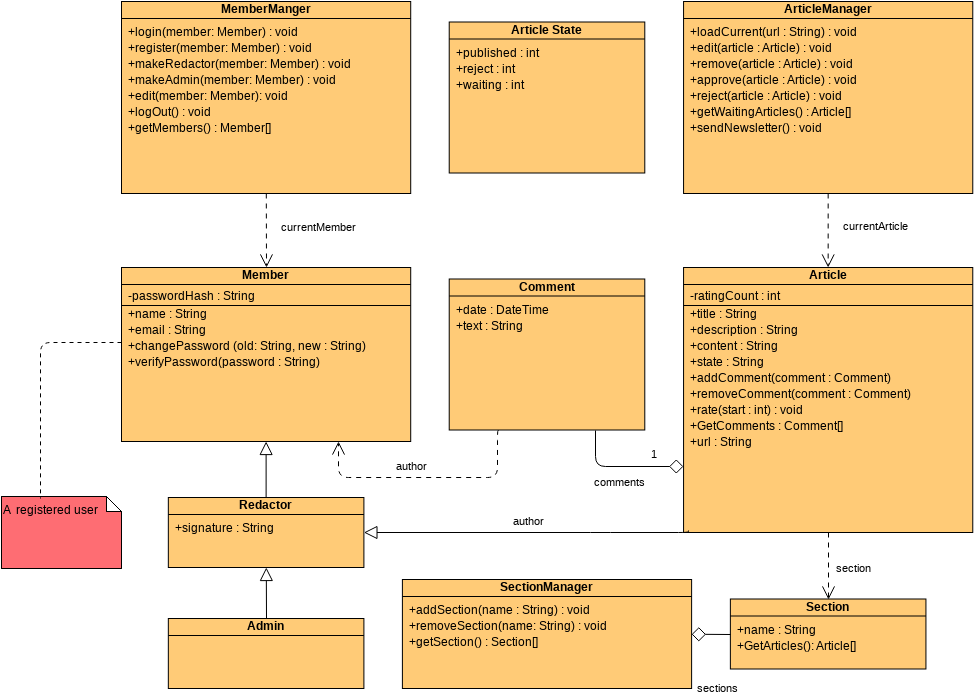
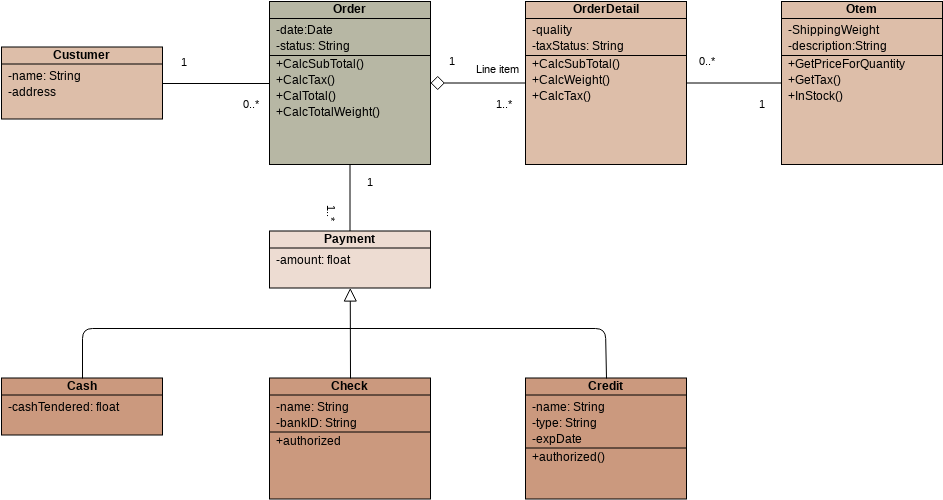
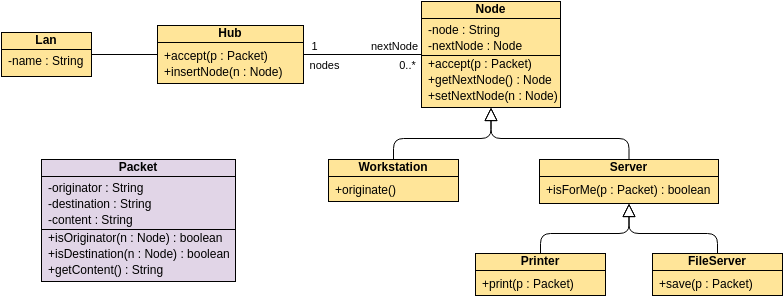
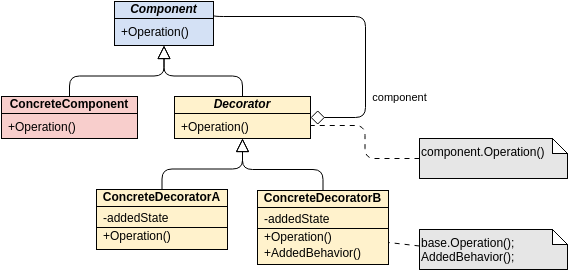
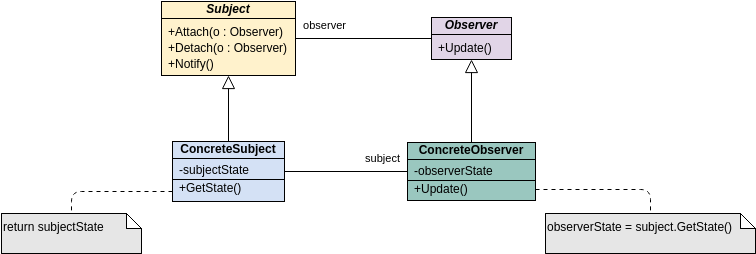
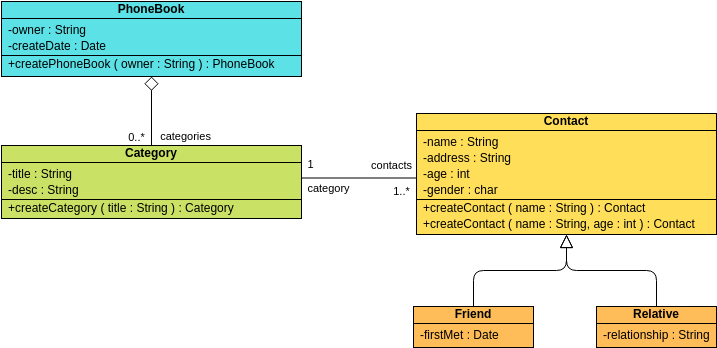
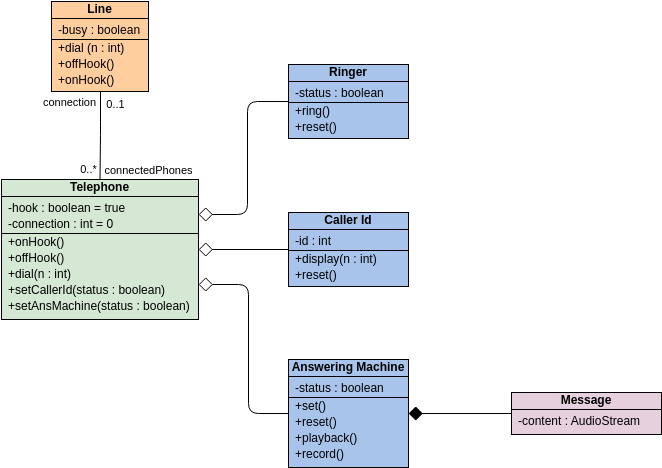
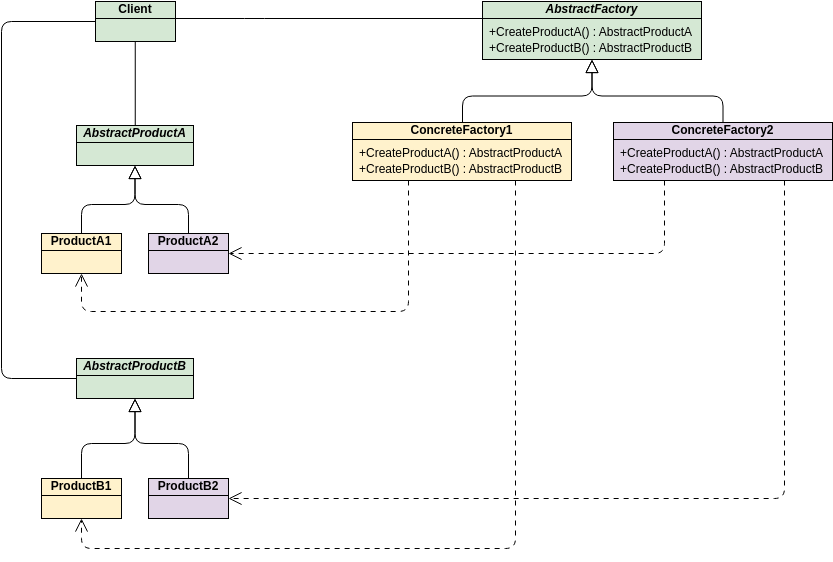
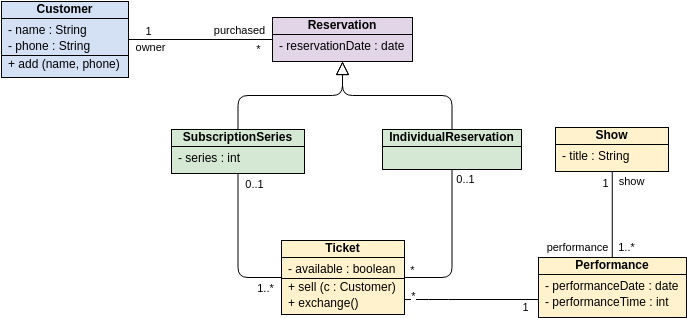
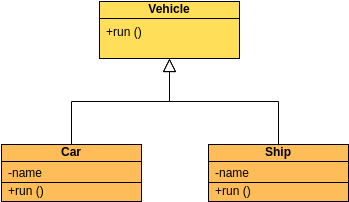
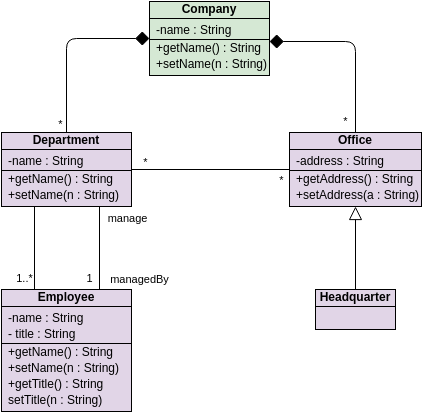
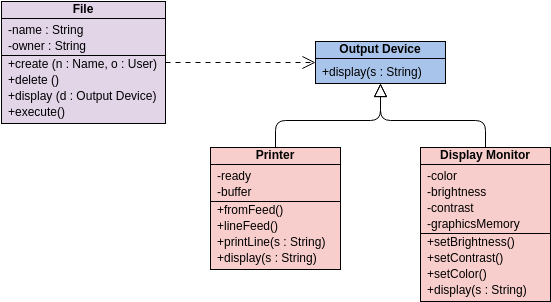
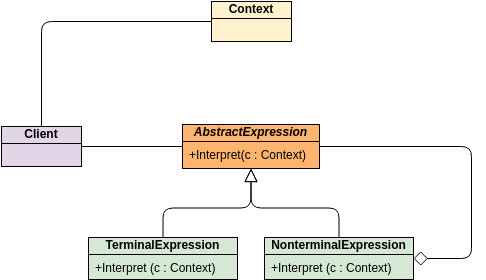
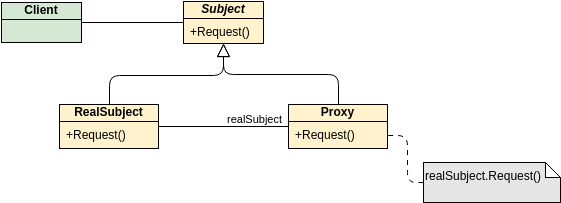
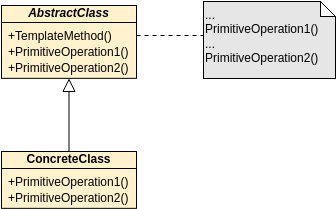
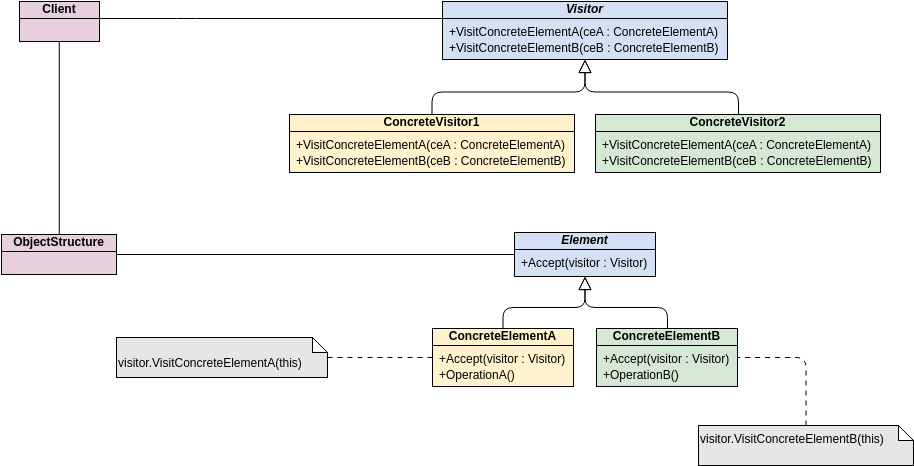
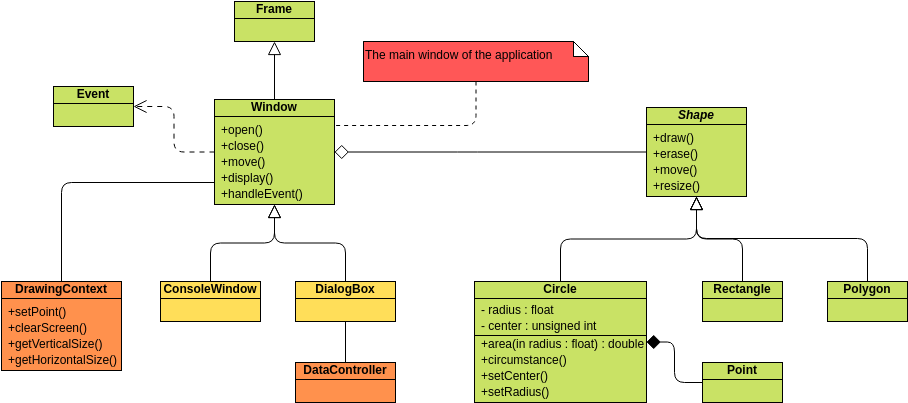
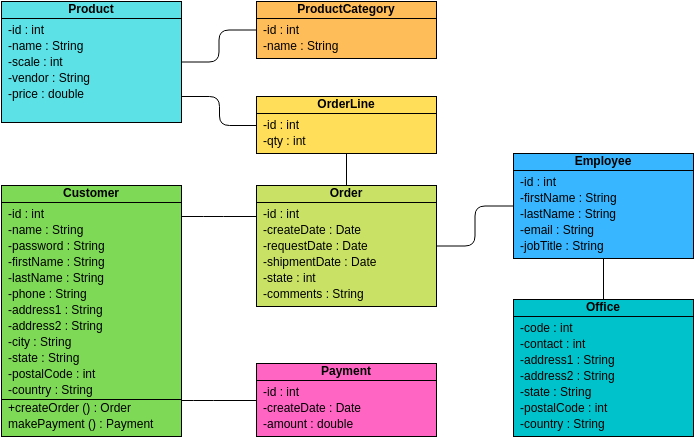
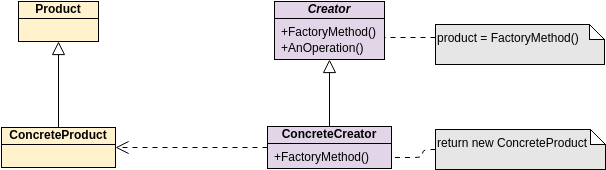
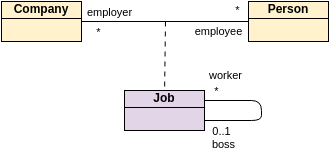
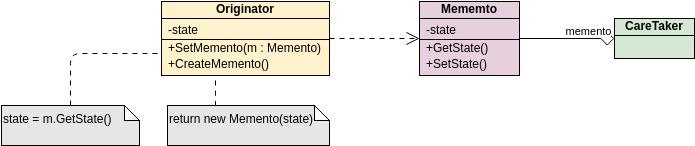
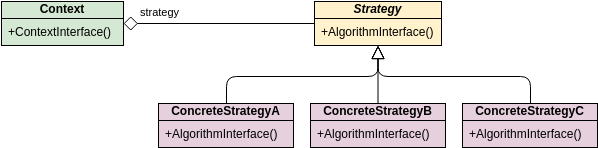
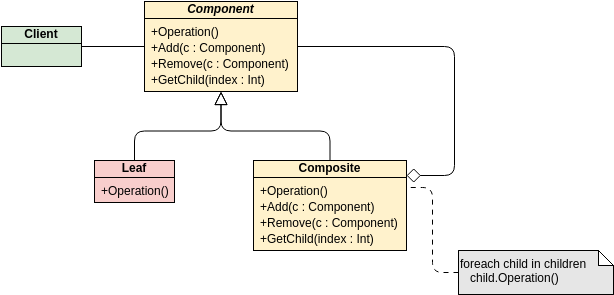
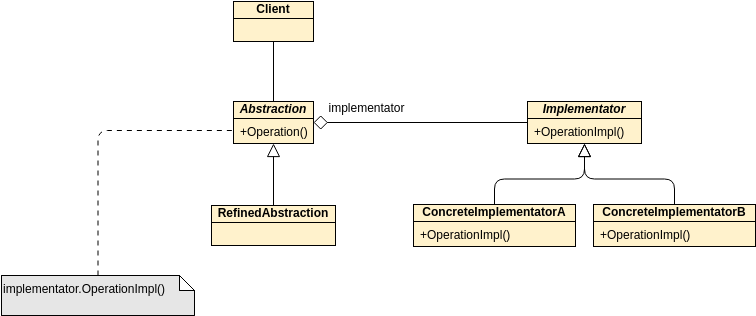
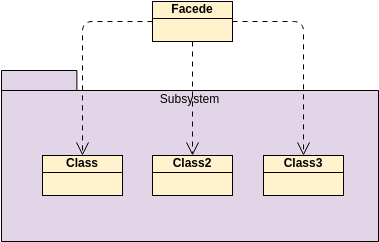
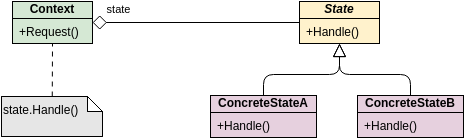
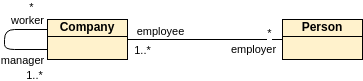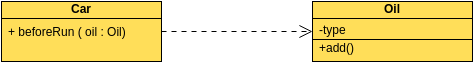Class diagrams are widely used in modeling object-oriented systems because they are the only UML diagrams that can be directly mapped to an object-oriented language.
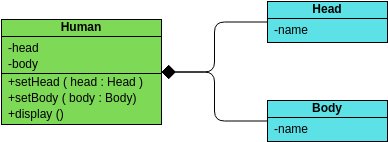
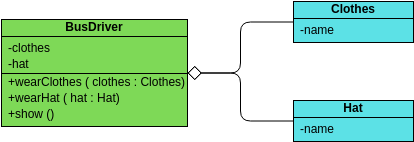
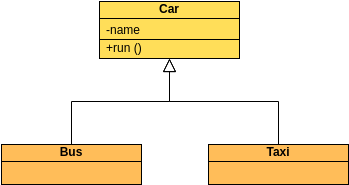
A class "Car" is depicted in the class diagram as a rectangle with three horizontal sections, as shown in the example.
The top section shows the name of the class (Car),
the middle section contains the properties of the class, and
the bottom section contains the operations (or "methods") of the class.
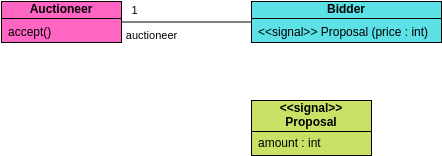
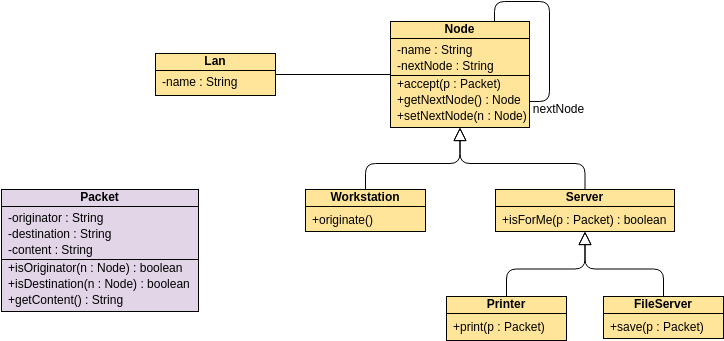
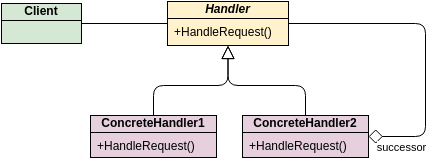
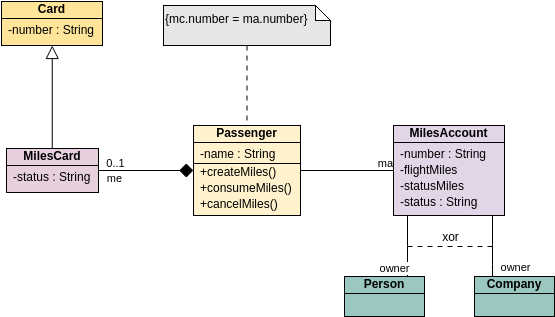
These are the different types of relationships between classes as shown in the Car example class diagram:
Associations - If two classes in a model need to communicate with each other, there must be a connection between them. The association can be represented in the class diagram by a line between these classes, with arrows indicating the navigation direction.
Multiplicity - multiplicity indicates how many instances of a class participate in the relationship. It is a constraint that specifies the cardinality range allowed between two classes.