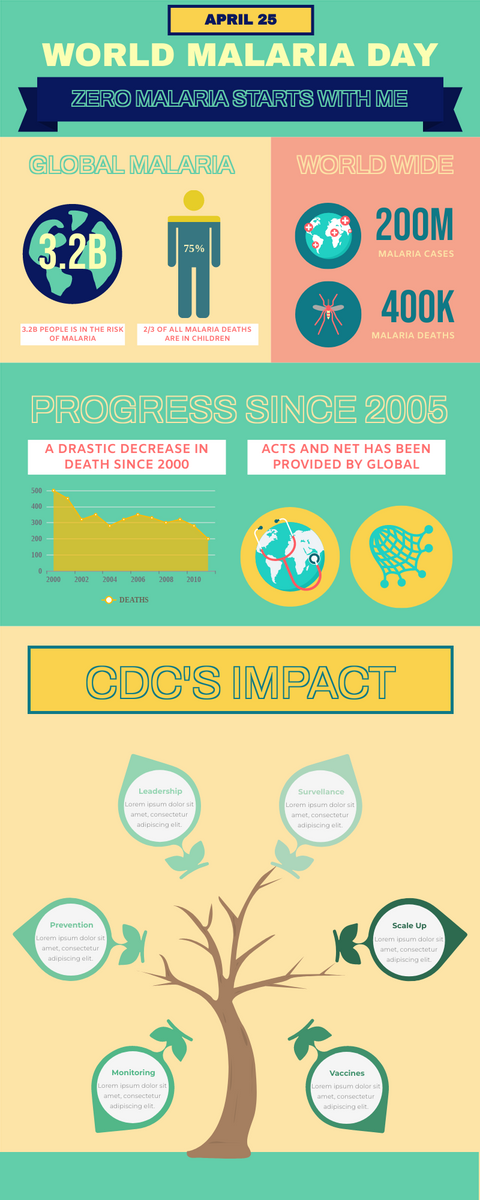
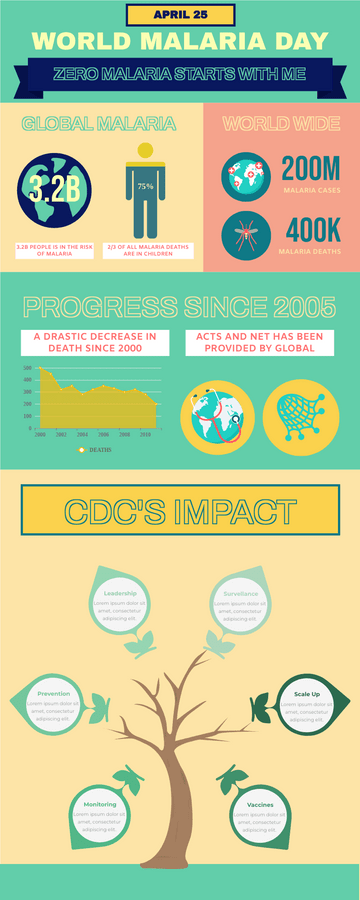
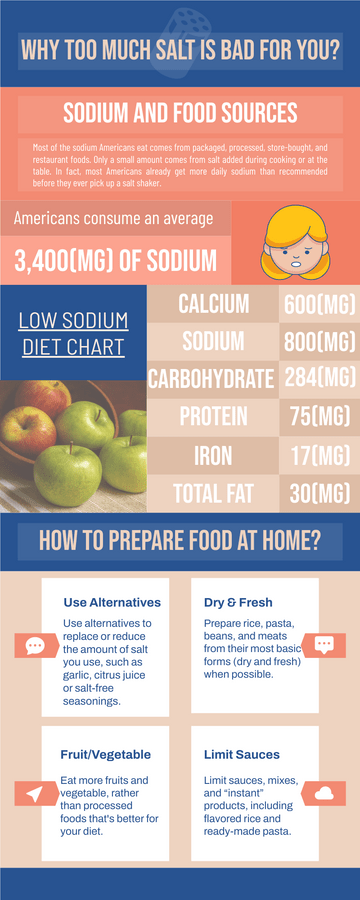
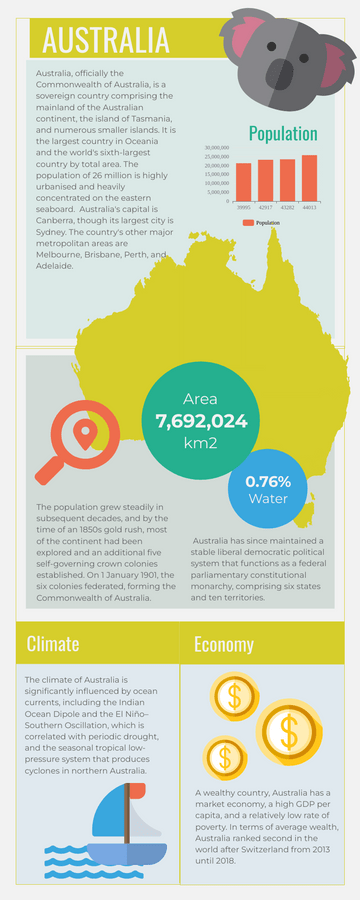
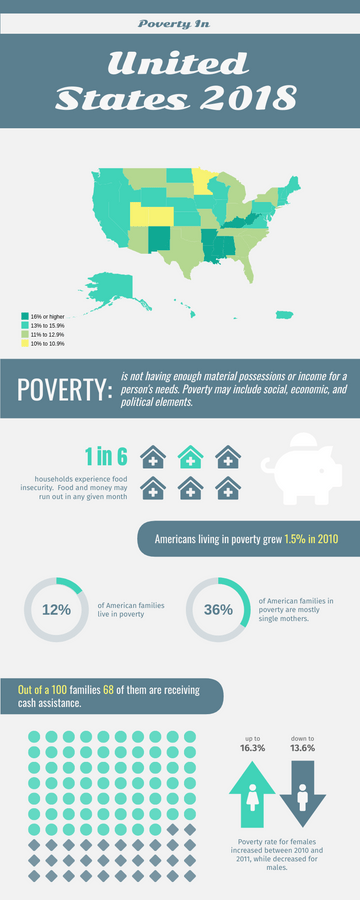
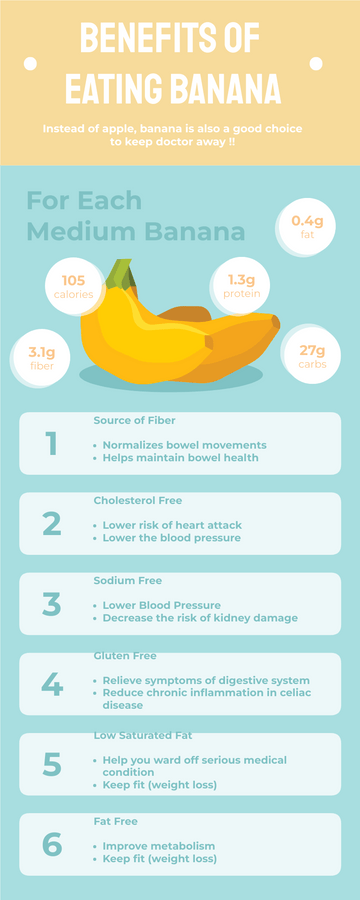
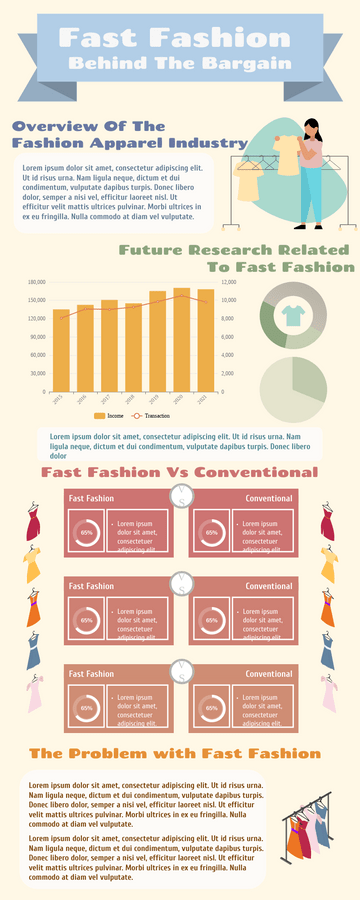
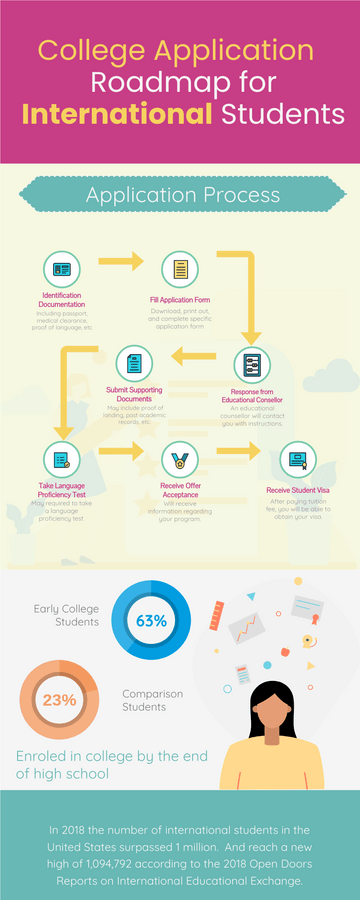
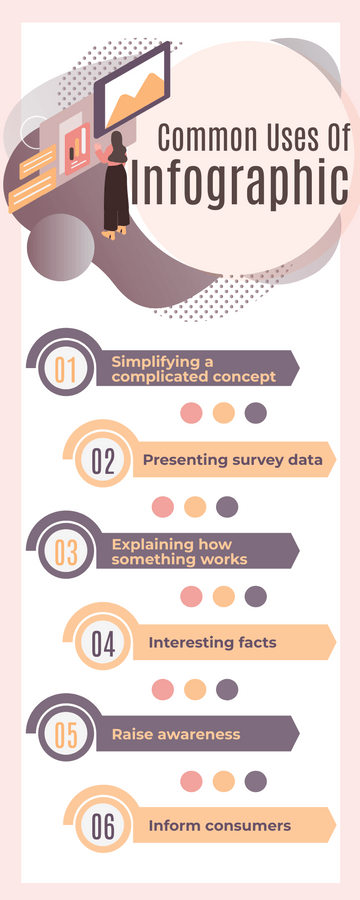
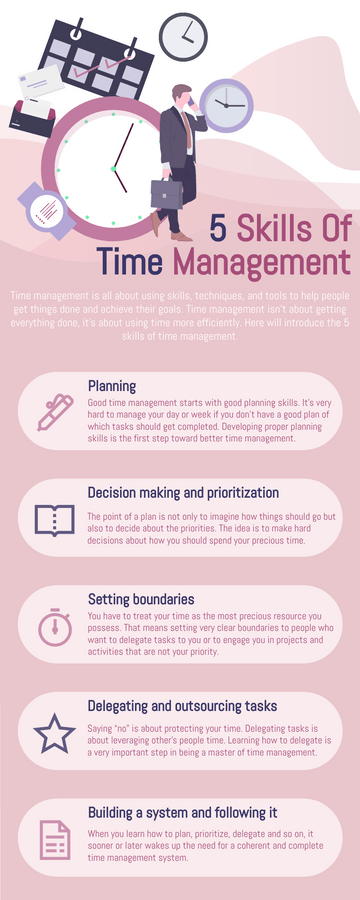
World Malaria Day Measures Infographic
Malaria is a disease caused by malaria parasites transmitted by malaria mosquitoes. The incubation period for malaria (from mosquito bite to disease) is about 7 to 30 days, some of which can last for months or more.
Symptoms of malaria include intermittent fever, chills, sweating, headache, tiredness, poor appetite and muscle pain.
In typical cases, the patient initially has a fever, then the heat subsides for one to three days, followed by a cycle of fever and fever.
Complications include anemia, liver and kidney failure, cramps, confusion and coma, which can lead to death if not treated early.
How does malaria spread?
Malaria is transmitted by the bite of a female malaria mosquito, which enters the body when the mosquito draws blood.
How to prevent malaria?
The most important and best way to prevent malaria is to avoid mosquito bites, as follows:
Always wear long-sleeved shirts and trousers;
Accommodation in an air-conditioned or mosquito-resistant area;
If there is no mosquito shelter or air-conditioning facilities in the accommodation, it is best to use mosquito repellent and sleep in mosquito nets;
Mosquito repellent, or DEET mosquito repellent, is found on exposed skin and clothing.
Travellers travelling to forested areas with malaria should bring mosquito nets and spray chlorpyrifos on clothing or mosquito nets for increased protection.